Early nasal type I IFN immunity against SARS-CoV-2 is compromised in patients with autoantibodies against type I IFNs
- PMID: 34357402
- PMCID: PMC8352718
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20211211
Early nasal type I IFN immunity against SARS-CoV-2 is compromised in patients with autoantibodies against type I IFNs
Erratum in
-
Correction: Early nasal type I IFN immunity against SARS-CoV-2 is compromised in patients with autoantibodies against type I IFNs.J Exp Med. 2021 Oct 4;218(10):jem.2021121108132021c. doi: 10.1084/jem.2021121108132021c. Epub 2021 Aug 20. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34415984 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
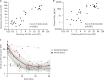
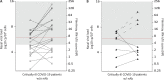
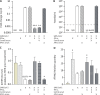
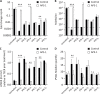
IFN-I and IFN-III immunity in the nasal mucosa is poorly characterized during SARS-CoV-2 infection. We analyze the nasal IFN-I/III signature, namely the expression of ISGF-3-dependent IFN-stimulated genes, in mildly symptomatic COVID-19 patients and show its correlation with serum IFN-α2 levels, which peak at symptom onset and return to baseline from day 10 onward. Moreover, the nasal IFN-I/III signature correlates with the nasopharyngeal viral load and is associated with the presence of infectious viruses. By contrast, we observe low nasal IFN-I/III scores despite high nasal viral loads in a subset of critically ill COVID-19 patients, which correlates with the presence of autoantibodies (auto-Abs) against IFN-I in both blood and nasopharyngeal mucosa. In addition, functional assays in a reconstituted human airway epithelium model of SARS-CoV-2 infection confirm the role of such auto-Abs in abrogating the antiviral effects of IFN-I, but not those of IFN-III. Thus, IFN-I auto-Abs may compromise not only systemic but also local antiviral IFN-I immunity at the early stages of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
© 2021 Lopez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: M. Mommert, W. Mouton, K. Brengel-Pesce, A. Bal, and V. Cheynet reported personal fees from bioMérieux during the conduct of the study and personal fees from bioMérieux outside the submitted work. M. Mommert, K. Brengel-Pesce, and S. Trouillet-Assant have a patent to FR2107421 pending. A. Pizzorno, B. Padey, and M. Rosa-Calatrava reported a patent to FR 20/02351 (Therapeutic treatments against SARS-CoV-2) pending. S. Trouillet-Assant and J.-B. Fassier reported non-financial support from bioMérieux during the conduct of the study and non-financial support from bioMérieux outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures








Comment in
-
The early interferon catches the SARS-CoV-2.J Exp Med. 2021 Oct 4;218(10):e20211667. doi: 10.1084/jem.20211667. Epub 2021 Aug 23. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34424267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bal, A., Trabaud M.-A., Fassier J.-B., Rabilloud M., Saker K., Langlois-Jacques C., Guibert N., Paul A., Alfaiate D., Massardier-Pilonchery A., et al. . COVID SER Study Group . 2021. Six-month antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 in healthcare workers assessed by virus neutralization and commercial assays. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 27:933–935. 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.01.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bastard, P., Rosen L.B., Zhang Q., Michailidis E., Hoffmann H.-H., Zhang Y., Dorgham K., Philippot Q., Rosain J., Béziat V., et al. . COVID Human Genetic Effort . 2020. Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science. 370:eabd4585. 10.1126/science.abd4585 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bastard, P., Michailidis E., Hoffmann H.-H., Chbihi M., Le Voyer T., Rosain J., Philippot Q., Seeleuthner Y., Gervais A., Materna M., et al. . 2021c. Auto-antibodies to type I IFNs can underlie adverse reactions to yellow fever live attenuated vaccine. J. Exp. Med. 218:e20202486. 10.1084/jem.20202486 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AI088364/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- EQU201903007798/French Foundation for Medical Research
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- Grandir - Fonds de solidarité pour l'enfance
- ANR-10-IAHU-01/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- École normale supérieure de Lyon
- JPB Foundation
- Fisher Center for Alzheimer's Research Foundation
- ANR-20-C11-0001/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- University of Paris
- George Mason University
- Institut National du Cancer
- Rockefeller University
- Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
- Meyer Foundation
- Fondation des Hospices Civils de Lyon
- Emergent Ventures
- ANRS-COV05/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- Hospices Civils de Lyon
- Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale
- UL1 TR001866/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- Square Foundation
- Claude Bernard Lyon 1 University
- Institut Mérieux
- R01 AI088364/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- SCOR Corporate Foundation for Science
- Fondation ARC (équipe labellisée)
- St. Giles Foundation
- REACTing
- ANR-20-COVI-0003/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- ANR-10-LABX-62-IBEID/Integrative Biology of Emerging Infectious Diseases Laboratory of Excellence
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

