Immunogenicity of subcutaneous TNF inhibitors and its clinical significance in real-life setting in patients with spondyloarthritis
- PMID: 34357455
- PMCID: PMC9124652
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-021-04955-8
Immunogenicity of subcutaneous TNF inhibitors and its clinical significance in real-life setting in patients with spondyloarthritis
Abstract
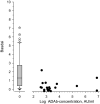
Considerable proportion of patients with SpA have been immunized to the subcutaneous anti-TNF drug they are using. Concomitant use of MTX protects from immunization, whereas SASP does not. Patients with SpA using subcutaneous anti-TNF drugs can benefit from monitoring of the drug trough levels. Immunization to biological drugs can lead to decreased efficacy and increased risk of adverse effects. The objective of this cross-sectional study was to assess the extent and significance of immunization to subcutaneous tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) patients in real-life setting. A serum sample was taken 1-2 days before the next drug injection. Drug trough concentrations, anti-drug antibodies (ADAb) and TNF-blocking capacity were measured in 273 patients with axSpA using subcutaneous anti-TNF drugs. The clinical activity of SpA was assessed using the Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) and the Maastricht AS Entheses Score (MASES). ADAb were found in 11% of the 273 patients: in 21/99 (21%) of patients who used adalimumab, in 0/83 (0%) of those who used etanercept, in 2/79 (3%) of those who used golimumab and in 6/12 (50%) of those who used certolizumab pegol. Use of methotrexate reduced the risk of formation of ADAb, whereas sulfasalazine did not. Presence of ADAb resulted in decreased drug concentration and reduced TNF-blocking capacity. However, low levels of ADAb had no effect on TNF-blocking capacity and did not correlate with disease activity. The drug trough levels were below the consensus target level in 36% of the patients. High BMI correlated with low drug trough concentration. Patients with low drug trough levels had higher disease activity. The presence of anti-drug antibodies was associated with reduced drug trough levels, and the patients with low drug trough levels had higher disease activity. The drug trough levels were below target level in significant proportion of patients and, thus, measuring the drug concentration and ADAb could help to optimize the treatment in SpA patients.
Keywords: Ankylosing spondylitis; Anti-drug antibodies; Biological therapy; Disease activity; Spondyloarthritis; Therapeutic drug monitoring.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Hiltunen reports non-financial support from Pfizer (congress costs), outside the submitted work. Dr. Parmanne reports non-financial support from Novartis, Pfizer and Abbvie, outside the submitted work. Dr. Sokka-Isler reports non-financial support from DiaGraphIT, personal fees from Abbvie, BMS, Celgene, Medac, Merck, Novartis, Orion Pharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, UCB and Bohringer Ingelheim, outside the submitted work. Dr. Isomäki reports personal fees and non-financial support from Abbvie, personal fees from Lilly, Pfizer, personal fees and non-financial support from Roche, outside the submitted work. Dr. Kaipiainen-Seppänen reports non-financial support from Novartis and Pfizer, outside the submitted work. Dr. Pirilä reports personal fees from Mylan Finland, Novartis Finland, Abbvie Oy, Boeringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Swedish Orphan Biotirum and Viatris, other support from Oriola Finland, Sanofi, Jansen Cilat and Eli Lilly Finland, outside the submitted work. Dr. Kauppi reports personal fees from Abbvie, Eli Lilly Finland, MSD, Novartis/Sandoz, Pfizer, Roche, UCB and Berlin-Chenie Menarini, outside the submitted work. Dr. Yli-Kerttula reports personal fees from MSD, Pfizer, BMS and Abbvie, outside the submitted work. Dr. Tuompo reports personal fees from Viatris, non-financial support from Novartis and Viatris, outside the submitted work. Dr. Relas reports personal fees from Abbvie, Celgene and Pfizer, outside the submitted work. Dr. Paalanen reports non-financial support from Celgene, Sandoz, non-financial support and other from Pfizer, personal fees and other from Orion Pharma, non-financial support and other support from MSD, non-financial support and other support from Medac, non-financial support and other support from Roche, non-financial support from Sanofi, outside the submitted work. Dr. Vidqvist reports personal fees (lecturer fees and advisory board): Abbvie, Boeringer-Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB. Dr. Tadesse reports non-financial support from Novartis, outside the submitted work. Dr. Borodina reports non-financial support from Novartis, Roche and Eli Lilly, outside the submitted work. Dr. Elfving reports personal fees from Abbvie (lecture fee) and Astra Zeneca (consultation fee), non-financial support from Pfizer and Mylan (congress costs), outside the submitted work. Dr. Rantalaiho reports congress grants from Mylan, Abbvie and Pfizer, and a study grant from BMS for NordStar trial, outside the submitted work. Dr. Jokiranta reports grants from Pfizer, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Abbvie, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Bristol- Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly Finland, Medac, Medscape, MSD, Novartis/Sandoz, Pfizer, Roche, Scopeful, Takeda, UCB, United Medix Laboratories and Tammer BioLab, outside the submitted work. Dr. Eklund reports grants from Pfizer, during the conduct of the study. PhD. Lamberg, Dr. Peltomaa, Dr Uutela, Dr. Taimen, Dr. Kortelainen, Dr. Asikainen, Dr. Ekman, Dr. Santisteban, Dr. Romu, Dr. Valleala, Dr. Leirisalo-Repo and Mr. Kautiainen have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

