The efficacy and safety of dupilumab in Chinese patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
- PMID: 34358343
- PMCID: PMC9298048
- DOI: 10.1111/bjd.20690
The efficacy and safety of dupilumab in Chinese patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Abstract
Background: Dupilumab is an antibody against interleukin-4 receptor α, used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD).
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adult Chinese patients with moderate-to-severe AD.
Methods: In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, phase III study, conducted between December 2018 and February 2020, patients with AD received dupilumab (300 mg) or placebo once every 2 weeks for 16 weeks, and were followed up for 12 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with both an Investigator's Global Assessment score of 0-1 and a reduction from baseline of ≥ 2 points at week 16.
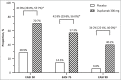
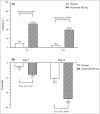
Results: Overall, 165 patients (mean age 30·6 years; 71·5% male patients) were randomized; 82 patients were randomized to dupilumab and 83 patients were randomized to placebo. At week 16, 26·8% of patients in the dupilumab group and 4·8% of patients in the placebo group achieved the primary endpoint [difference 22·0%, 95% confidence interval (CI) 11·37-32·65; P < 0·001]. Compared with placebo, higher proportions of patients in the dupilumab group achieved ≥ 75% reduction in the Eczema Area and Severity Index score (57·3% vs. 14·5%; difference 42·9%, 95% CI 29·75-55·97; P < 0·001) and had ≥ 3-point (52·4% vs. 9·6%; difference 42·8%, 95% CI 30·26-55·34; P < 0·001) and ≥ 4-point (39·0% vs. 4·8%; difference 34·2%, 95% CI 22·69-45·72; P < 0·001) reductions in weekly average daily peak daily pruritus numerical rating scale scores. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events during the treatment period was similar in the two groups. The incidence of conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis and injection site reaction was higher in the dupilumab group than in the placebo group.
Conclusions: In adult Chinese patients, dupilumab was effective in improving the signs and symptoms of AD and demonstrated a favourable safety profile.
© 2021 Sanofi. British Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists.
Figures


References
-
- Chiesa Fuxench ZC, Block JK, Boguniewicz M et al. Atopic dermatitis in America study: a cross‐sectional study examining the prevalence and disease burden of atopic dermatitis in the US adult population. J Invest Dermatol 2019; 139:583–90. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg JI. Comorbidities and the impact of atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2019; 123:144–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

