Detection of Tumor Recurrence via Circulating Tumor DNA Profiling in Patients with Localized Lung Cancer: Clinical Considerations and Challenges
- PMID: 34359659
- PMCID: PMC8345193
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13153759
Detection of Tumor Recurrence via Circulating Tumor DNA Profiling in Patients with Localized Lung Cancer: Clinical Considerations and Challenges
Abstract
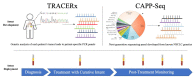
Approximately 30% of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) present with localized/non-metastatic disease and are eligible for surgical resection or other "treatment with curative intent". Due to the high prevalence of recurrence after treatment, adjuvant therapy is standard care for most patients. The effect of adjuvant chemotherapy is, however, modest, and new tools are needed to identify candidates for adjuvant treatments (chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies), especially since expanded lung cancer screening programs will increase the rate of patients detected with localized NSCLC. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has shown strong potential to detect minimal residual disease (MRD) and to guide adjuvant therapies. In this manuscript, we review the technical aspects and performances of the main ctDNA sequencing platforms (TRACERx, CAPP-seq) investigated in this purpose, and discuss the potential of this approach to guide or spare adjuvant therapies after definitive treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: NSCLC; circulating tumor DNA; liquid biopsy; minimal residual disease; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ettinger D.S., Wood D.E., Aisner D.L., Akerley W., Bauman J., Chirieac L.R., D’Amico T.A., DeCamp M.M., Dilling T.J., Dobelbower M., et al. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 5.2017, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017;15:504–535. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2017.0050. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

