Extracellular Vesicles in Advanced Prostate Cancer: Tools to Predict and Thwart Therapeutic Resistance
- PMID: 34359692
- PMCID: PMC8345194
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13153791
Extracellular Vesicles in Advanced Prostate Cancer: Tools to Predict and Thwart Therapeutic Resistance
Abstract
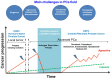
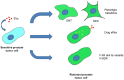
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most frequent cancer and the fifth leading cause of cancer death among men worldwide. At first, advanced PCa is treated by androgen deprivation therapy with a good initial response. Nevertheless, recurrences occur, leading to Castrate-Resistance Prostate Cancer (CRPC). During the last decade, new therapies based on inhibition of the androgen receptor pathway or taxane chemotherapies have been used to treat CRPC patients leading to an increase in overall survival, but the occurrence of resistances limits their benefits. Numerous studies have demonstrated the implication of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in different cancer cellular mechanisms. Thus, the possibility to isolate and explore EVs produced by tumor cells in plasma/sera represents an important opportunity for the deciphering of those mechanisms and the discovery of biomarkers. Herein, we summarized the role of EVs in therapeutic resistance of advanced prostate cancer and their use to find biomarkers able to predict these resistances.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; predictive biomarkers; prostate cancer; therapeutic resistances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploitation of the Androgen Receptor to Overcome Taxane Resistance in Advanced Prostate Cancer.Adv Cancer Res. 2015;127:123-58. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Adv Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26093899 Review.
-
Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Dec;140(3):223-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23859952 Review.
-
NPRL2 enhances autophagy and the resistance to Everolimus in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Prostate. 2019 Jan;79(1):44-53. doi: 10.1002/pros.23709. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Prostate. 2019. PMID: 30178500
-
Extracellular Vesicles in the Adaptive Process of Prostate Cancer during Inhibition of Androgen Receptor Signaling by Enzalutamide.Proteomics. 2017 Dec;17(23-24). doi: 10.1002/pmic.201600427. Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 29105980
-
Serum testosterone level as possible predictive marker in androgen receptor axis-targeting agents and taxane chemotherapies for castration-resistant prostate cancer.Urol Oncol. 2019 Mar;37(3):180.e19-180.e24. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.10.020. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Urol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30446464
Cited by
-
Transcript Markers from Urinary Extracellular Vesicles for Predicting Risk Reclassification of Prostate Cancer Patients on Active Surveillance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 4;16(13):2453. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132453. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001515 Free PMC article.
-
AK-I-190, a New Catalytic Inhibitor of Topoisomerase II with Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Activity on Androgen-Negative Prostate Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 18;22(20):11246. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011246. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681904 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Nucleolin and Associated Genes in Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 19;23(9):4491. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094491. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35562881 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Extracellular Vesicles in Prostate and Renal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 28;24(19):14713. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914713. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834162 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gravis G., Fizazi K., Joly F., Oudard S., Priou F., Esterni B., Latorzeff I., Delva R., Krakowski I., Laguerre B., et al. Androgen-deprivation therapy alone or with docetaxel in non-castrate metastatic prostate cancer (GETUG-AFU 15): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:149–158. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70560-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

