ENDOG Impacts on Tumor Cell Proliferation and Tumor Prognosis in the Context of PI3K/PTEN Pathway Status
- PMID: 34359707
- PMCID: PMC8345062
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13153803
ENDOG Impacts on Tumor Cell Proliferation and Tumor Prognosis in the Context of PI3K/PTEN Pathway Status
Abstract
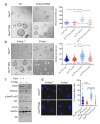
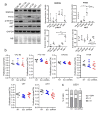
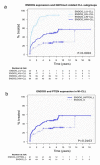
EndoG influences mitochondrial DNA replication and is involved in somatic cell proliferation. Here, we investigated the effect of ENDOG/Endog expression on proliferation in different tumor models. Noteworthy, ENDOG deficiency reduced proliferation of endometrial tumor cells expressing low PTEN/high p-AKT levels, and Endog deletion blunted the growth of PTEN-deficient 3D endometrial cultures. Furthermore, ENDOG silencing reduced proliferation of follicular thyroid carcinoma and glioblastoma cell lines with high p-AKT expression. High ENDOG expression was associated with a short time to treatment in a cohort of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), a B-cell lymphoid neoplasm with activation of PI3K/AKT. This clinical impact was observed in the less aggressive CLL subtype with mutated IGHV in which high ENDOG and low PTEN levels were associated with worse outcome. In summary, our results show that reducing ENDOG expression hinders growth of some tumors characterized by low PTEN activity and high p-AKT expression and that ENDOG has prognostic value for some cancer types.
Keywords: AKT; ENDOG; PTEN; chronic lymphocytic leukemia; endometrial carcinoma; glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rozenblatt-Rosen O., Regev A., Oberdoerffer P., Nawy T., Hupalowska A., Rood J.E., Ashenberg O., Cerami E., Coffey R.J., Demir E., et al. The Human Tumor Atlas Network: Charting Tumor Transitions across Space and Time at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell. 2020;181:236–249. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blasco N., Cámara Y., Núñez E., Beà A., Barés G., Forné C., Ruíz-Meana M., Girón C., Barba I., García-Arumí E., et al. Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by Endonuclease G deficiency requires reactive oxygen radicals accumulation and is inhibitable by the micropeptide humanin. Redox Biol. 2018;16:146–156. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.02.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- SAF2013-44942-R; PID2019-104509RB-I00; SAF2016-80157-R; PID2019-104734RB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- 20153810; 201920-30/Fundació la Marató de TV3
- ICGC-CLL Genome Project/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI15/00551/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- 2014-SGR-795/Agència de Gestió d'Ajuts Universitaris i de Recerca
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

