The Global Interest in Vaccines and Its Prediction and Perspectives in the Era of COVID-19. Real-Time Surveillance Using Google Trends
- PMID: 34360134
- PMCID: PMC8345601
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18157841
The Global Interest in Vaccines and Its Prediction and Perspectives in the Era of COVID-19. Real-Time Surveillance Using Google Trends
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has globally overwhelmed all sectors of life. The fast development of vaccines against COVID-19 has had a significant impact on the course of the pandemic.
Methods: Global data from Google Trends was analyzed for vaccines against flu, BCG, HPV, pneumococcal disease, polio, and COVID-19. The time frame includes the last five-year period starting from 17 April 2016. Multiple training of time series models with back testing, including Holt-Winters forecasting, Exponential Smoothing State Space, Linear model with trend and seasonal components (tlsm), and ARIMA was conducted. Forecasting according to the best fitting model was performed.
Results: Correlation analysis did not reveal a decrease in interest in vaccines during the analyzed period. The prediction models provided a short-term forecast of the dynamics of interest for flu, HPV, pneumococcal and polio vaccines with 5-10% growth in interest for the first quarter of 2022 when compared to the same quarter of 2021.
Conclusions: Despite the huge interest in the COVID-19 vaccine, there has not been a detectable decline in the overall interest in the five analyzed vaccines.
Keywords: BCG vaccine; COVID-19 vaccine; Google Trends; HPV vaccine; Polio vaccine; flu vaccine; pneumococcal vaccine; vaccination programs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
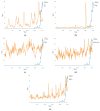


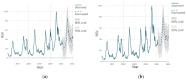
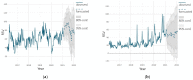
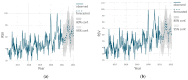
References
-
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19. [(accessed on 28 May 2021)];2020 Mar 11; Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera....
-
- Worldometer—COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. [(accessed on 28 June 2021)]; Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?utm_campaign=homeAdvegas1.
-
- WHO COVID-19 Vaccines. [(accessed on 29 May 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/covid-19....
-
- WHO Immunization in the Context of COVID-19 Pandemic. [(accessed on 28 May 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/immunization-in-the-context-of-c....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

