Novel Therapeutic Approaches for Alzheimer's Disease: An Updated Review
- PMID: 34360973
- PMCID: PMC8348485
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22158208
Novel Therapeutic Approaches for Alzheimer's Disease: An Updated Review
Abstract
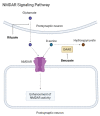
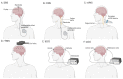
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease and accounts for most cases of dementia. The prevalence of AD has increased in the current rapidly aging society and contributes to a heavy burden on families and society. Despite the profound impact of AD, current treatments are unable to achieve satisfactory therapeutic effects or stop the progression of the disease. Finding novel treatments for AD has become urgent. In this paper, we reviewed novel therapeutic approaches in five categories: anti-amyloid therapy, anti-tau therapy, anti-neuroinflammatory therapy, neuroprotective agents including N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor modulators, and brain stimulation. The trend of therapeutic development is shifting from a single pathological target to a more complex mechanism, such as the neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative processes. While drug repositioning may accelerate pharmacological development, non-pharmacological interventions, especially repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), also have the potential for clinical application. In the future, it is possible for physicians to choose appropriate interventions individually on the basis of precision medicine.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; NMDA; amyloid; brain stimulation; neuroinflammation; neuroprotection; precision medicine; rTMS; tDCS; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest concerning this article.
Figures

References
-
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division World Population Ageing 2020 Highlights: Living Arrangements of Older Persons. [(accessed on 4 April 2021)];2020 (ST/ESA/SER.A/451) Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/sites/www.un.org.development.desa....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

