The 3,4-Quinones of Estrone and Estradiol Are the Initiators of Cancer whereas Resveratrol and N-acetylcysteine Are the Preventers
- PMID: 34361004
- PMCID: PMC8347442
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22158238
The 3,4-Quinones of Estrone and Estradiol Are the Initiators of Cancer whereas Resveratrol and N-acetylcysteine Are the Preventers
Abstract
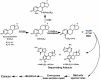
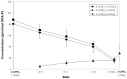
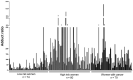
This article reviews evidence suggesting that a common mechanism of initiation leads to the development of many prevalent types of cancer. Endogenous estrogens, in the form of catechol estrogen-3,4-quinones, play a central role in this pathway of cancer initiation. The catechol estrogen-3,4-quinones react with specific purine bases in DNA to form depurinating estrogen-DNA adducts that generate apurinic sites. The apurinic sites can then lead to cancer-causing mutations. The process of cancer initiation has been demonstrated using results from test tube reactions, cultured mammalian cells, and human subjects. Increased amounts of estrogen-DNA adducts are found not only in people with several different types of cancer but also in women at high risk for breast cancer, indicating that the formation of adducts is on the pathway to cancer initiation. Two compounds, resveratrol, and N-acetylcysteine, are particularly good at preventing the formation of estrogen-DNA adducts in humans and are, thus, potential cancer-prevention compounds.
Keywords: N-acetylcysteine; cancer initiation; cancer prevention; estrogen-DNA adducts; estrogens; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The molecular etiology and prevention of estrogen-initiated cancers: Ockham's Razor: Pluralitas non est ponenda sine necessitate. Plurality should not be posited without necessity.Mol Aspects Med. 2014 Apr;36:1-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Mol Aspects Med. 2014. PMID: 23994691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depurinating estrogen-DNA adducts, generators of cancer initiation: their minimization leads to cancer prevention.Clin Transl Med. 2016 Mar;5(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40169-016-0088-3. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Clin Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 26979321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical depurinating DNA adducts: Estrogen adducts in the etiology and prevention of cancer and dopamine adducts in the etiology and prevention of Parkinson's disease.Int J Cancer. 2017 Sep 15;141(6):1078-1090. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30728. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28388839 Review.
-
Catechol quinones of estrogens in the initiation of breast, prostate, and other human cancers: keynote lecture.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Nov;1089:286-301. doi: 10.1196/annals.1386.042. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17261777
-
Catechol estrogen quinones as initiators of breast and other human cancers: implications for biomarkers of susceptibility and cancer prevention.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1766(1):63-78. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.03.001. Epub 2006 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16675129 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Cytochrome P450 Cancer-Related Metabolic Activities and Gene Polymorphisms: A Review.Cells. 2024 Nov 26;13(23):1958. doi: 10.3390/cells13231958. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39682707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Susceptibility to Colorectal Cancer Based on HSD17B4 rs721673 and rs721675 Polymorphisms and Alcohol Intake among Taiwan Biobank Participants: A Retrospective Case Control Study Using the Nationwide Claims Data.J Pers Med. 2023 Mar 24;13(4):576. doi: 10.3390/jpm13040576. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37108962 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Estrogen Metabolites and Risk of Breast Cancer among Postmenopausal Women in the Nurses' Health Study.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2025 Mar 3;34(3):375-384. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-24-0577. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2025. PMID: 39190182 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect and Molecular Mechanism of the Estrogen Signaling Pathway.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 12;11:763539. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.763539. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35096574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estetrol: From Preclinical to Clinical Pharmacology and Advances in the Understanding of the Molecular Mechanism of Action.Drugs R D. 2023 Jun;23(2):77-92. doi: 10.1007/s40268-023-00419-5. Epub 2023 May 3. Drugs R D. 2023. PMID: 37133685 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bosland M.C., Ford H., Horton L. Induction at high incidence of ductal prostate adenocarcinomas in NBL/Cr and Sprague-Dawley Hsd:SD rats treated with a combination of testosterone and estradiol-17β or diethylstilbestrol. Carcinogenesis. 1995;16:1311–1317. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.6.1311. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rohrmann S., Nelson W.G., Rifari N., Brown T.R., Dobs A., Kanarek N., Yager J.D., Platz E.A. Serum estrogen, but not testosterone, levels differ between black and white men in a nationally representative sample of Americans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007;92:2519–2525. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0028. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

