Co-Treatment of Copper Oxide Nanoparticle and Carbofuran Enhances Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish Embryos
- PMID: 34361024
- PMCID: PMC8435221
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22158259
Co-Treatment of Copper Oxide Nanoparticle and Carbofuran Enhances Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
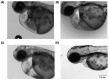
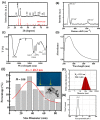
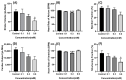
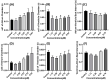
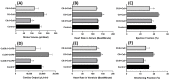
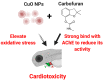
The use of chemicals to boost food production increases as human consumption also increases. The insectidal, nematicidal and acaricidal chemical carbofuran (CAF), is among the highly toxic carbamate pesticide used today. Alongside, copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO) are also used as pesticides due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. The overuse of these pesticides may lead to leaching into the aquatic environments and could potentially cause adverse effects to aquatic animals. The aim of this study is to assess the effects of carbofuran and copper oxide nanoparticles into the cardiovascular system of zebrafish and unveil the mechanism behind them. We found that a combination of copper oxide nanoparticle and carbofuran increases cardiac edema in zebrafish larvae and disturbs cardiac rhythm of zebrafish. Furthermore, molecular docking data show that carbofuran inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity in silico, thus leading to impair cardiac rhythms. Overall, our data suggest that copper oxide nanoparticle and carbofuran combinations work synergistically to enhance toxicity on the cardiovascular performance of zebrafish larvae.
Keywords: CuO nanoparticle; carbofuran; cardiotoxicity; molecular docking; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures








References
-
- Edwards C.A. Nature and origins of pollution of aquatic systems by pesticides. In: Khan M.A., editor. Pesticides in Aquatic Environments. Springer; Boston, MA, USA: 1977. pp. 11–38.
-
- Aznar-Alemany Ò., Eljarrat E. Bioavailability and bioaccumulation of pyrethroid insecticides in wildlife and humans. Pyrethroid Insectic. 2020:205–225. doi: 10.1007/698_2020_466. - DOI
-
- Jonathan B., Maina H., Barminas J. Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in five Fish Speciesin the Vicinity of Lake Chad, Baga, Nigerian Sector. Asian J. Sci. Technol. 2020;11:10631–10633.
-
- Fakhri Y., Nematollahi A., Abdi-Moghadam Z., Daraei H., Ghasemi S.M. Concentration of Potentially Harmful Elements (PHEs) in Trout Fillet (Rainbow and Brown) Fish: A Global Systematic Review and Meta-analysis and Health Risk Assessment. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020;199:3089–3101. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02419-x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

