Recent Advances of Photocatalytic Application in Water Treatment: A Review
- PMID: 34361190
- PMCID: PMC8308214
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11071804
Recent Advances of Photocatalytic Application in Water Treatment: A Review
Abstract
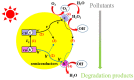
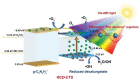
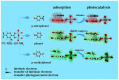
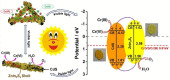
Photocatalysis holds great promise as an efficient and sustainable oxidation technology for application in wastewater treatment. Rapid progress developing novel materials has propelled photocatalysis to the forefront of sustainable wastewater treatments. This review presents the latest progress on applications of photocatalytic wastewater treatment. Our focus is on strategies for improving performance. Challenges and outlooks in this promising field are also discussed. We hope this review will help researchers design low-cost and high-efficiency photocatalysts for water treatment.
Keywords: disinfection; heavy metal; photocatalysis; semiconductors; wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

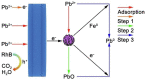

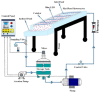
References
-
- Gómez-Pastora J., Dominguez S., Bringas E., Rivero M.J., Ortiz I., Dionysiou D.D. Review and perspectives on the use of magnetic nanophotocatalysts (MNPCs) in water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;310:407–427. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.140. - DOI
-
- World-Water-Development-Report. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization; Paris, France: 2020.
-
- Zularisam A.W., Ismail A.F., Salim R. Behaviours of natural organic matter in membrane filtration for surface water treatment-a review. Desalination. 2006;194:211–231. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2005.10.030. - DOI
-
- Azimi A., Azari A., Rezakazemi M., Ansarpour M. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: A review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017;4:37–59. doi: 10.1002/cben.201600010. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

