Effect of Structural Differences on the Mechanical Properties of 3D Integrated Woven Spacer Sandwich Composites
- PMID: 34361484
- PMCID: PMC8348545
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14154284
Effect of Structural Differences on the Mechanical Properties of 3D Integrated Woven Spacer Sandwich Composites
Abstract
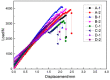
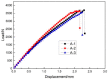
Three-dimensional integrated woven spacer sandwich composites have been widely used as industrial textiles for many applications due to their superior physical and mechanical properties. In this research, 3D integrated woven spacer sandwich composites of five different specifications were produced, and the mechanical properties and performance were investigated under different load conditions. XR-CT (X-ray computed tomography) images were employed to visualize the microstructural details and analyze the fracture morphologies of fractured specimens under different load conditions. In addition, the effects of warp and weft direction, face sheet thickness, and core pile height on the mechanical properties and performance of the composite materials were analyzed. This investigation can provide significant guidance to help determine the structure of composite materials and design new products according to the required mechanical properties.
Keywords: 3D integrated woven spacer sandwich composites; X-ray computed tomography; designing new products; industrial textiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






















References
-
- Velosa J.C., Rana S., Fangueiro R., Van Hattum F.W.J., Soutinho F., Marques S. Mechanical behavior of novel sandwich composite panels based on 3D-knitted spacer fabrics. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2012;31:95–105. doi: 10.1177/0731684411431354. - DOI
-
- Khosravani M.R. Applied Mechanics and Materials. Trans Tech Publications; Kapellweg, Switzerland: 2012. Composite materials manufacturing processes; pp. 1361–1367.
-
- Sugun B.S., Sundaram R. 3D Composites: Opportunities & Challenges. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2015;95:221–232.
-
- Jia L.X., Wang R., Liu J.M. Design and Property Analysis of Woven Spacer Fabric Sandwich Panels. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011;332–334:747–751. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.332-334.747. - DOI
-
- Li M., Wang S., Zhang Z., Wu B. Effect of Structure on the Mechanical Behaviors of Three-Dimensional Spacer Fabric Composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2009;16:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s10443-008-9072-4. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

