Evaluation of Stresses on Implant, Bone, and Restorative Materials Caused by Different Opposing Arch Materials in Hybrid Prosthetic Restorations Using the All-on-4 Technique
- PMID: 34361502
- PMCID: PMC8348490
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14154308
Evaluation of Stresses on Implant, Bone, and Restorative Materials Caused by Different Opposing Arch Materials in Hybrid Prosthetic Restorations Using the All-on-4 Technique
Abstract
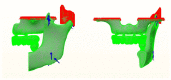
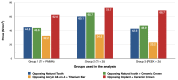
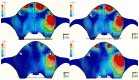
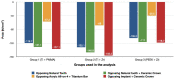
The long-term success of dental implants is greatly influenced by the use of appropriate materials while applying the "All-on-4" concept in the edentulous jaw. This study aims to evaluate the stress distribution in the "All-on-4" prosthesis across different material combinations using three-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA) and to evaluate which opposing arch material has destructive effects on which prosthetic material while offering certain recommendations to clinicians accordingly. Acrylic and ceramic-based hybrid prosthesis have been modelled on a rehabilitated maxilla using the "All-on-4" protocol. Using different materials and different supports in the opposing arch (natural tooth, and implant/ceramic, and acrylic), a multi-vectorial load has been applied. To measure stresses in bone, maximum and minimum principal stress values were calculated, while Von Mises stress values were obtained for prosthetic materials. Within a single group, the use of an acrylic implant-supported prosthesis as an antagonist to a full arch implant-supported prosthesis yielded lower maximum (Pmax) and minimum (Pmin) principal stresses in cortical bone. Between different groups, maxillary prosthesis with polyetheretherketone as framework material showed the lowest stress values among other maxillary prostheses. The use of rigid materials with higher moduli of elasticity may transfer higher stresses to the peri implant bone. Thus, the use of more flexible materials such as acrylic and polyetheretherketone could result in lower stresses, especially upon atrophic bones.
Keywords: All-on-4®; finite element analysis; hybrid prosthesis; implant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





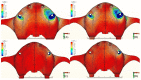
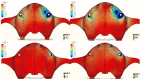

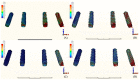
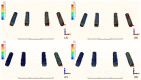
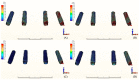

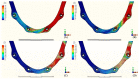
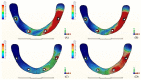

References
-
- Papaspyridakos P., Chen C.-J., Chuang S.-K., Weber H.-P., Gallucci G. A systematic review of biologic and technical complications with fixed implant rehabilitations for edentulous patients. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012;27:102–110. - PubMed
-
- Fischer K., Stenberg T. Prospective 10-Year Cohort Study Based on a Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) on Implant-Supported Full-Arch Maxillary Prostheses. Part 1: Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Implants and Mucosal Tissue. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2011;14:808–815. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2011.00389.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

