Novel Bifunctional [16]aneS4-Derived Chelators for Soft Radiometals
- PMID: 34361752
- PMCID: PMC8348053
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26154603
Novel Bifunctional [16]aneS4-Derived Chelators for Soft Radiometals
Abstract
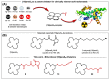
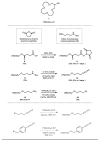
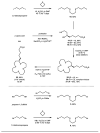
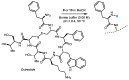
The field of targeted radionuclide therapy is rapidly growing, highlighting the need for wider radionuclide availability. Soft Lewis acid ions, such as radioisotopes of platinum, rhodium and palladium, are particularly underdeveloped. This is due in part to a lack of compatible bifunctional chelators. These allow for the practical bioconjugation to targeting vectors, in turn enabling radiolabeling. The [16]andS4 macrocycle has been reported to chelate a number of relevant soft metal ions. In this work, we present a procedure for synthesizing [16]andS4 in 45% yield (five steps, 12% overall yield), together with a selection of strategies for preparing bifunctional derivatives. An ester-linked N-hydroxysuccimide ester (NHS, seven steps, 4% overall yield), an ether-linked isothiocyanate (NCS, eight steps, 5% overall yield) and an azide derivative were prepared. In addition, a new route to a carbon-carbon linked carboxylic acid functionalized derivative is presented. Finally, a general method for conjugating the NHS and NCS derivatives to a polar peptide (octreotide) is presented, by dissolution in water:acetonitrile (1:1), buffered to pH 9.4 using borate. The reported compounds will be readily applicable in radiopharmaceutical chemistry, by facilitating the labeling of a range of molecules, including peptides, with relevant soft radiometal ions.
Keywords: bifunctional chelators; bio-conjugation; radiation therapy; sulfur containing macrocycles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Novartis.com. [(accessed on 25 June 2021)]; Available online: https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/novartis-announces-positive....
-
- Knapp F.F., Dash A. Radiopharmaceuticals for Therapy. 1st ed. Springer; New Delhi, India: 2016.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

