Evaluation of Antioxidative Mechanisms In Vitro and Triterpenes Composition of Extracts from Silver Birch (Betula pendula Roth) and Black Birch (Betula obscura Kotula) Barks by FT-IR and HPLC-PDA
- PMID: 34361786
- PMCID: PMC8347892
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26154633
Evaluation of Antioxidative Mechanisms In Vitro and Triterpenes Composition of Extracts from Silver Birch (Betula pendula Roth) and Black Birch (Betula obscura Kotula) Barks by FT-IR and HPLC-PDA
Abstract
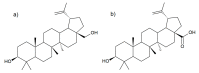
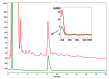
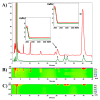
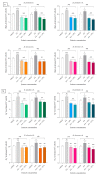
Silver birch, Betula pendula Roth, is one of the most common trees in Europe. Due to its content of many biologically active substances, it has long been used in medicine and cosmetics, unlike the rare black birch, Betula obscura Kotula. The aim of the study was therefore to compare the antioxidant properties of extracts from the inner and outer bark layers of both birch trees towards the L929 line treated with acetaldehyde. Based on the lactate dehydrogenase test and the MTT test, 10 and 25% concentrations of extracts were selected for the antioxidant evaluation. All extracts at tested concentrations reduced the production of hydrogen peroxide, superoxide anion radical, and 25% extract decreased malonic aldehyde formation in acetaldehyde-treated cells. The chemical composition of bark extracts was accessed by IR and HPLC-PDA methods and surprisingly, revealed a high content of betulin and lupeol in the inner bark extract of B. obscura. Furthermore, IR analysis revealed differences in the chemical composition of the outer bark between black and silver birch extracts, indicating that black birch may be a valuable source of numerous biologically active substances. Further experiments are required to evaluate their potential against neuroinflammation, cancer, viral infections, as well as their usefulness in cosmetology.
Keywords: Betula obscura Kotula; Betula pendula Roth; black birch; pentacyclic triterpenes; silver birch.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mashentseva A.A., Dehaen W., Seitembetov T.S., Seitembetova A.J. Comparison of the Antioxidant Activity of the Different Betula pendula Roth. Extracts from Northern Kazakhstan. J. Phytol. 2011;3:18–25.
-
- Fischer A., Lindner M., Abs C., Lasch P. Vegetation dynamics in central European forest ecosystems (near-natural as well as managed) after storm events. Folia Geobot. 2002;37:17–32. doi: 10.1007/BF02803188. - DOI
-
- Mircea T., Carmen P., Anda P. The analysis of flavonoids from indigenous species of Betulaceae. Farmacia. 2008;56:556–562.
-
- Ferreira J.P.A., Quilhó T., Pereira H. Characterization of Betula pendula Outer Bark Regarding Cork and Phloem Components at Chemical and Structural Levels in View of Biorefinery Integration. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2017;37:10–25. doi: 10.1080/02773813.2016.1224248. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

