A Large Retrospective Assessment of Voriconazole Exposure in Patients Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
- PMID: 34361978
- PMCID: PMC8303158
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9071543
A Large Retrospective Assessment of Voriconazole Exposure in Patients Treated with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
Abstract
Background: Voriconazole is one of the first-line therapies for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Drug concentrations might be significantly influenced by the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). We aimed to assess the effect of ECMO on voriconazole exposure in a large patient population.
Methods: Critically ill patients from eight centers in four countries treated with voriconazole during ECMO support were included in this retrospective study. Voriconazole concentrations were collected in a period on ECMO and before/after ECMO treatment. Multivariate analyses were performed to evaluate the effect of ECMO on voriconazole exposure and to assess the impact of possible saturation of the circuit's binding sites over time.
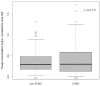
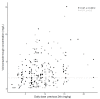
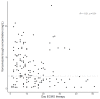
Results: Sixty-nine patients and 337 samples (190 during and 147 before/after ECMO) were analyzed. Subtherapeutic concentrations (<2 mg/L) were observed in 56% of the samples during ECMO and 39% without ECMO (p = 0.80). The median trough concentration, for a similar daily dose, was 2.4 (1.2-4.7) mg/L under ECMO and 2.5 (1.4-3.9) mg/L without ECMO (p = 0.58). Extensive inter-and intrasubject variability were observed. Neither ECMO nor squared day of ECMO (saturation) were retained as significant covariates on voriconazole exposure.
Conclusions: No significant ECMO-effect was observed on voriconazole exposure. A large proportion of patients had voriconazole subtherapeutic concentrations.
Keywords: critically ill patients; exposure; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; invasive fungal infections; pharmacokinetics; therapeutic drug monitoring; variability; voriconazole.
Conflict of interest statement
LMB discloses the following conflicts of interest; Eurosets Srl., Medolla, Italy (Medical Advisory Board); Xenios AG, Heilbronn, Germany (Medical Advisory Board). AS has received non-financial support from Gilead Sciences and Pfizer, outside the context of this work. HF received honoraria for speaking at symposia from Pfizer but not related to the work under consideration. JW received speakers fee from MSD, Pfizer and Gilead, consultancy fee from Gilead and he obtained investigator-initiated grants from Gilead, Pfizer and MSD. IS is supported by the Clinical Research Fund of UZ Leuven and served as a consultant to and has received unrestricted travel and research grants from Gilead Sciences, Merck Sharpe and Dohme Corp., and Pfizer, Inc and Cidara. All contracts were through and invoiced by UZ and KU Leuven. RVD, BB, ML, BR, NGMH, PJ, FST, CACS, LMJ, PFL, EN, VG, AR, BP, PM, YD and CVDB have no conflicts of interest to declare related to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Patterson T.F., Thompson G.R., 3rd, Denning D.W., Fishman J.A., Hadley S., Herbrecht R., Kontoyiannis D.P., Marr K.A., Morrison V.A., Nguyen M.H., et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2016;63:e1–e60. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw326. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

