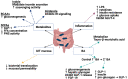
Gut microbiota influence in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)
- PMID: 34362432
- PMCID: PMC8343927
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-021-00446-0
Gut microbiota influence in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)
Abstract
A strong and expanding evidence base supports the influence of gut microbiota in human metabolism. Altered glucose homeostasis is associated with altered gut microbiota, and is clearly associated with the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and associated complications. Understanding the causal association between gut microbiota and metabolic risk has the potential role of identifying susceptible individuals to allow early targeted intervention.
Keywords: Gut microbiota; Type two diabetes mellitus.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or non-financial competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, Ninth Edition. 2019. https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/. Accessed 01 Mar 2021.
-
- World Health Organisation. Global Report on Diabetes. 2016. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565257. Accessed 01 Mar 2021.
-
- United Nations General Assembly. Political declaration of the high-level meeting of the general assembly on the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases. 2012. https://www.who.int/nmh/events/un_ncd_summit2011/political_declaration_e.... Accessed 01 Mar 2021.
-
- : Diabetes UK, Facts and Stats (2019). https://www.diabetes.org.uk/resources-s3/2019-02/1362B_Facts%20and%20sta.... Accessed 01 Mar 2021.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources