Arsenene-mediated multiple independently targeted reactive oxygen species burst for cancer therapy
- PMID: 34362904
- PMCID: PMC8346549
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24961-5
Arsenene-mediated multiple independently targeted reactive oxygen species burst for cancer therapy
Abstract
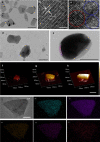
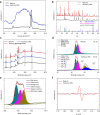
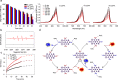
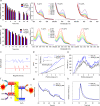
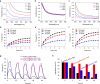
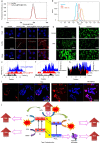
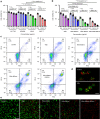
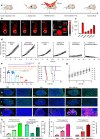
The modulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels is crucial for cellular homeostasis and determination of cellular fate. A sublethal level of ROS sustains cell proliferation, differentiation and promotes tumor metastasis, while a drastic ROS burst directly induces apoptosis. Herein, surface-oxidized arsenene nanosheets (As/AsxOy NSs) with type II heterojunction are fabricated with efficient ·O2- and 1O2 production and glutathione consumption through prolonging the lifetime of photo-excited electron-hole pairs. Moreover, the portion of AsxOy with oxygen vacancies not only catalyzes a Fenton-like reaction, generating ·OH and O2 from H2O2, but also inactivates main anti-oxidants to cut off the "retreat routes" of ROS. After polydopamine (PDA) and cancer cell membrane (M) coating, the engineered As/AsxOy@PDA@M NSs serve as an intelligent theranostic platform with active tumor targeting and long-term blood circulation. Given its narrow-band-gap-enabled in vivo fluorescence imaging properties, As/AsxOy@PDA@M NSs could be applied as an imaging-guided non-invasive and real-time nanomedicine for cancer therapy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

