Testing individual and pooled saliva samples for sars-cov-2 nucleic acid: a prospective study
- PMID: 34364098
- PMCID: PMC8279932
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115478
Testing individual and pooled saliva samples for sars-cov-2 nucleic acid: a prospective study
Abstract
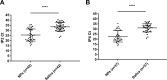
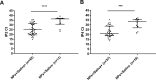
Control of the rapid spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus requires efficient testing. We collected paired nasopharyngeal swab (NPs) and saliva samples from 303 subjects (52.8% symptomatic) at a drive-through testing center; 18% of whom tested positive. The NPs, salivas and five saliva pools were tested for SARS-CoV-2 RNA using the Aptima™ assay and a laboratory-developed test (LDT) on the Panther-Fusion™ Hologic® platform. The saliva sensitivity was 80% (LDT) and 87.5% (Aptima™) whereas that of NPs was 96.4% in both assays. The pooled saliva sensitivity of 72.7% (LDT) and 75% (Aptima™) was not significantly different of that of individual saliva testing. Saliva specimens appear to be suitable for sensitive non-invasive assays to detect SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid; pooling them for a single test will improve laboratory throughput.
Keywords: COVID-19; Nasopharyngeal swabs; Pooling; RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2; Saliva; TMA.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Barat B, Das S, Giorgi VD, Henderson DK, Kopka S, Lau AF, et al. Pooled Saliva Specimens for SARS-CoV-2 Testing. J Clin Microbiol [Internet] 2021;59(3):e02486–20. https://jcm.asm.org/content/early/2020/11/30/JCM.02486-20 [cited 2020 Dec 12]. Available. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berenger BM, Conly JM, Fonseca K, Hu J, Louie T, Schneider AR, et al. Saliva collected in universal transport media is an effective, simple and high-volume amenable method to detect SARS-CoV-2. Clin Microbiol Infect [Internet] 2021;27(4):656–657. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7641592 [cited 2020 Nov 27]. Available. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

