Exosomes as cell-derivative carriers in the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system diseases
- PMID: 34365576
- PMCID: PMC8942947
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-021-01026-0
Exosomes as cell-derivative carriers in the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system diseases
Abstract
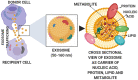
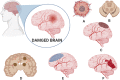
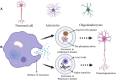
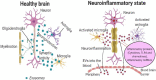
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles with the diameter ranging from 50 to 100 nm and are found in different body fluids such as blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), urine and saliva. Like in case of various diseases, based on the parent cells, the content of exosomes (protein, mRNA, miRNA, DNA, lipids and metabolites) varies and thus can be utilized as potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of the brain diseases. Furthermore, utilizing the natural potential exosomes to cross the blood-brain barrier and by specifically decorating it with the ligand as per the desired brain sites therapeutics can be delivered to brain parenchyma. This review article conveys the importance of exosomes and their use in the treatment and diagnosis of brain/central nervous system diseases.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; CNS diseases; Diagnosis; Exosomes; Targeted delivery.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rousseau M, Belleannee C, Duchez AC, Cloutier N, Levesque T, Jacques F, et al. Detection and quantification of microparticles from different cellular lineages using flow cytometry. Evaluation of the impact of secreted phospholipase A2 on microparticle assessment. PLOS ONE. 2015;10(1):e0116812. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meldolesi J. Exosomes and ectosomes in intercellular communication. Curr Biol. 2018;28(8):R435–R444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

