Strategies to deliver RNA by nanoparticles for therapeutic potential
- PMID: 34366123
- PMCID: PMC8792155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2021.100991
Strategies to deliver RNA by nanoparticles for therapeutic potential
Abstract
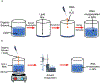
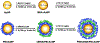
The use of a variety of RNA molecules, including messenger RNA, small interfering RNA, and microRNA, has shown great potential for prevention and therapy of many pathologies. However, this therapeutic promise has historically been limited by short in vivo half-life, lack of targeted delivery, and safety issues. Nanoparticle (NP)-mediated delivery has been a successful platform to overcome these limitations, with multiple formulations already in clinical trials and approved by the FDA. Although there is a diversity of NPs in terms of material formulation, size, shape, and charge that have been proposed for biomedical applications, specific modifications are required to facilitate sufficient RNA delivery and adequate therapeutic effect. This includes optimization of (i) RNA incorporation into NPs, (ii) specific cell targeting, (iii) cellular uptake and (iv) endosomal escape ability. In this review, we summarize the methods by which NPs can be modified for RNA delivery to achieve optimal therapeutic effects.
Keywords: Cellular uptake; Drug delivery; Endosomal escape; Nanomedicine; RNA therapy; Targeting.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

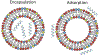
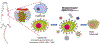


References
-
- Aali E, Shokuhi Rad A, & Esfahanian M (2020). Computational investigation of the strategy of DNA/RNA stabilization through the study of the conjugation of an oligonucleotide with silver and gold nanoparticles []. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 34(8), e5690. 10.1002/aoc.5690 - DOI
-
- Agency, E. M. (2018). Assessment report for Onpattro. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/onpattro-epar-p...
-
- Amos H (1961). Protamine enhancement of RNA uptake by cultured chick cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 5(1), 1–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

