rhKGF-2 Attenuates Smoke Inhalation Lung Injury of Rats via Activating PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and Repressing FoxO1-NLRP3 Inflammasome
- PMID: 34366838
- PMCID: PMC8339412
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.641308
rhKGF-2 Attenuates Smoke Inhalation Lung Injury of Rats via Activating PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and Repressing FoxO1-NLRP3 Inflammasome
Abstract
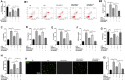
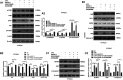
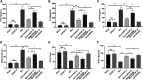
Smoke inhalation injury is an acute pathological change caused by thermal stimulation or toxic substance absorption through respiratory epithelial cells. This study aims to probe the protective effect and mechanism of recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor 2 (rhKGF-2) against smoke inhalation-induced lung injury (SILI) in rats. The SILI was induced in rats using a smoke exposure model, which were then treated with rhKGF-2. The rat blood was collected for blood-gas analysis, and the levels of inflammatory factors and oxidative stress markers in the plasma were measured. The rat lung tissues were collected. The pathological changes and cell apoptosis were determined by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining and TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay, and the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1, and FoxO1-NLRP3 inflammasome expression were verified by western blot (WB). Both of the human alveolar epithelial cell (HPAEpiC) and primary rat alveolar epithelial cell were exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for making in-vitro alveolar epithelial cell injury model. After treatment with rhKGF-2, GSK2126458 (PI3K inhibitor) and AS1842856 (FoxO1 inhibitor), the cell viability, apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, reactive oxygen species (ROS), PI3K/Akt/Nrf2, HO-1/NQO1, and FoxO1-NLRP3 in HPAEpiC and primary rat alveolar epithelial cell were examined. The data suggested that rhKGF-2 reduced LPS-induced HPAEpiC cell and primary rat alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis and the expression of inflammatory factors and oxidative stress factors. Moreover, rhKGF-2 improved the blood gas and alleviated SILI-induced lung histopathological injury in vivo via repressing inflammation, NLRP3 inflammasome activation and oxidative stress. Mechanistically, rhKGF-2 activated PI3K/Akt pathway, enhanced Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 expression, and attenuated FoxO1-NLRP3 inflammasome both in vitro and in vivo. However, pharmaceutical inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway attenuated rhKGF-2-mediated protective effects against SILI, while suppressing FoxO1 promoted rhKGF-2-mediated protective effects. Taken together, this study demonstrated that rhKGF-2 mitigated SILI by regulating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway and the FoxO1-NLRP3 axis, which provides new reference in treating SILI.
Keywords: FoxO1; NLRP3; PI3K; inflammation; rhKGF-2; smoke inhalation injury.
Copyright © 2021 Fu, Jiang, Guo, Liao, Liu and Xiong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Effects of aerosol inhalation of recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor 2 on the lung tissue of rabbits with severe smoke inhalation injury].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018 Jul 20;34(7):466-475. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2018.07.009. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30060349 Chinese.
-
Pirfenidone alleviates smoke inhalation lung injury of rats via the NF-κB signaling pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Nov;12(11):e70014. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70014. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39588955 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Let-7f-1-3p attenuates smoke-induced apoptosis in bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells in vitro by targeting FOXO1.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 5;862:172531. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172531. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31301310
-
Baicalin Reduces Renal Inflammation in Mesangial Proliferative Glomerulonephritis through Activation of Nrf2/ARE and PI3K/AKT Pathways.Discov Med. 2023 Jun;35(176):372-382. doi: 10.24976/Discov.Med.202335176.38. Discov Med. 2023. PMID: 37272104
-
Deciphering the molecular mechanism of NLRP3 in BPA-mediated toxicity: Implications for targeted therapies.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 30;10(7):e28917. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28917. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38596095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the AMPK/Nrf2 Pathway: A Novel Therapeutic Approach for Acute Lung Injury.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 15;17:4683-4700. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S467882. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39051049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3-methyladenine ameliorates acute lung injury by inhibiting oxidative damage and apoptosis.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 2;10(13):e33996. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33996. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39055838 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary delivery of resveratrol-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes for the prevention of zinc chloride smoke-induced acute lung injury.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):1122-1131. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2048135. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35380089 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Linoleic Acid Intake Becomes a Risk Factor for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by Affecting Ovarian Granulosa Cells.FASEB J. 2025 Apr 15;39(7):e70518. doi: 10.1096/fj.202402648RR. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40197608 Free PMC article.
-
Linoleic acid induces human ovarian granulosa cell inflammation and apoptosis through the ER-FOXO1-ROS-NFκB pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 16;14(1):6392. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56970-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38493198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J., Wang Z. G., Zheng Z. M., Chen Y., Khor S., Shi K., et al. (2017). Neuron and Microglia/macrophage-Derived FGF10 Activate Neuronal FGFR2/PI3K/Akt Signaling and Inhibit Microglia/macrophages TLR4/NF-κb-dependent Neuroinflammation to Improve Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Death Dis 8 (10), e3090. 10.1038/cddis.2017.490 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

