Anti-Obesity and Lipid Lowering Activity of Bauhiniastatin-1 is Mediated Through PPAR-γ/AMPK Expressions in Diet-Induced Obese Rat Model
- PMID: 34366856
- PMCID: PMC8341109
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.704074
Anti-Obesity and Lipid Lowering Activity of Bauhiniastatin-1 is Mediated Through PPAR-γ/AMPK Expressions in Diet-Induced Obese Rat Model
Abstract
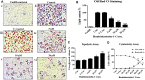
Objective: To evaluate the therapeutic efficacy and underlying molecular mechanisms of Bauhiniastatin-1 (BSTN1) to alleviate adiposity in diet-induced obese rodent model and in 3T3-L1 cells. Methods: BSTN1 was purified and confirmed through HPLC. In-vitro experiments such as MTT assay, Oil Red-O (ORO) stain, cellular lipid content, glycerol release and RT-PCR analysis were performed in 3T3-L1 cells in the presence and absence of BSTN1. In animal experiments, rats were divided into Group-I: normal pellet diet-fed, Group-II: HFD-fed, Groups-III, IV and V: HFD-fed BSTN1 (1.25, 2.5, and 5 mg/kg.b.wt./day/rat)-treated and Group-VI: HFD-fed Orlistat-treated. The rats were fed either normal diet or high fat diet (HFD) for 18 weeks and water ad-libitum. BSTN1 was orally administered from 13th week onwards to the selected HFD-fed groups. Body composition parameters, biochemical assays, histopathology examination and western blot analysis were performed to identify the predicted targets related to obesity. Molecular docking studies threw light on the binding interactions of BSTN1 against PPAR-γ, FAS and AMPK. Results: BSTN1 at 20 μM significantly (p < 0.001) inhibited adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells. A conspicuous down-regulation in the mRNA expression levels of PPAR-γ, FAS and SREBP1 was observed but AMPK expression remained unchanged in BSTN1 treated 3T3-L1 cells. A substantial decrease in body weight gain, fat percent, total body fat, serum and liver lipid profile (except high-density lipoprotein), glucose, insulin and insulin resistance in BSTN1 treated rats was noticed in a dose dependent manner. In BSTN1 (5 mg/kg.b.wt.)-treated groups significantly (p < 0.01) elevated plasma adiponectin level but reduced leptin level as well as fall in serum AST and ALT were noticed. Further, the disturbed structural integrity and architecture of adipose and hepatic tissues due to high fat diet feeding were considerably recovered with BSTN1 treatment. Down-regulation in the protein expression level of PPAR-γ and activation of AMPK through phosphorylation was observed in BSTN1 treated rats than the untreated. Molecular docking studies revealed strong binding interactions of BSTN1 against PPAR-γ and AMPK and thus supported the experimental results. Conclusion: Taken together, the results suggest that BSTN1 could be a promising pharmacological molecule in the treatment of obesity and dyslipidemia.
Keywords: 3T3-L1 cells; AMPK; PPAR-γ; adipogenesis; bauhiniastatin-1; diet-induced obesity; insulin resistance; molecular docking.
Copyright © 2021 Karunakaran, Lokanatha, Muni Swamy, Venkataramaiah, Muni Kesavulu, Appa Rao, Badri and Balaji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Thymoquinone mitigates obesity and diabetic parameters through regulation of major adipokines, key lipid metabolizing enzymes and AMPK/p-AMPK in diet-induced obese rats.3 Biotech. 2024 Jan;14(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03847-x. Epub 2023 Dec 18. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38125651 Free PMC article.
-
The Herbal Medicine KBH-1 Inhibits Fat Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and Reduces High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity through Regulation of the AMPK Pathway.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 9;10(12):e0142041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142041. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26649747 Free PMC article.
-
Acer tegmentosum Maxim Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3t3-l1 Adipocytes and Attenuates Lipid Accumulation in Obese Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 7;12(12):3753. doi: 10.3390/nu12123753. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33297378 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the antiadipogenic-antiobesity effects of a rice hull smoke extract in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cells and in mice on a high-fat diet.Food Funct. 2015 Sep;6(9):2939-48. doi: 10.1039/c5fo00469a. Food Funct. 2015. PMID: 26190448
-
Ilex paraguariensis A.St.-Hil. improves lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-fed obese rats and suppresses intracellular lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via the AMPK-dependent and insulin signaling pathways.Food Nutr Res. 2024 Jan 22;68. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v68.10307. eCollection 2024. Food Nutr Res. 2024. PMID: 38327997 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biogenic Phytochemicals Modulating Obesity: From Molecular Mechanism to Preventive and Therapeutic Approaches.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 27;2022:6852276. doi: 10.1155/2022/6852276. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35388304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymoquinone mitigates obesity and diabetic parameters through regulation of major adipokines, key lipid metabolizing enzymes and AMPK/p-AMPK in diet-induced obese rats.3 Biotech. 2024 Jan;14(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03847-x. Epub 2023 Dec 18. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 38125651 Free PMC article.
-
Cornelian Cherry (Cornus mas L.) Fruit Extract Lowers SREBP-1c and C/EBPα in Liver and Alters Various PPAR-α, PPAR-γ, LXR-α Target Genes in Cholesterol-Rich Diet Rabbit Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 18;25(2):1199. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021199. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256272 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Adipogenic and Anti-Obesity Effects of Gongmi Tea and Gongmi So Extract.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023 Mar 31;28(1):21-29. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.1.21. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37066032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badri K. R., Zhou Y., Dhru U., Aramgam S., Schuger L. (2008). Effects of the SANT Domain of Tension-Induced/inhibited Proteins (TIPs), Novel Partners of the Histone Acetyltransferase P300, on P300 Activity and TIP-6-Induced Adipogenesis. Mol. Cel Biol 28, 6358–6372. 10.1128/MCB.00333-08 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

