Matrine Impairs Platelet Function and Thrombosis and Inhibits ROS Production
- PMID: 34366869
- PMCID: PMC8339414
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.717725
Matrine Impairs Platelet Function and Thrombosis and Inhibits ROS Production
Abstract
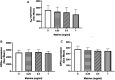
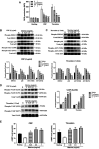
Matrine is a naturally occurring alkaloid and possesses a wide range of pharmacological properties, such as anti-cancer, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory effects. However, whether it affects platelet function and thrombosis remains unclear. This study aims to evaluate the effect of matrine on platelet function and thrombus formation. Human platelets were treated with matrine (0-1 mg/ml) for 1 h at 37°C followed by measuring platelet aggregation, granule secretion, receptor expression by flow cytometry, spreading and clot retraction. In addition, matrine (10 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally into mice to measure tail bleeding time, arterial and venous thrombus formation. Matrine dose-dependently inhibited platelet aggregation and ATP release in response to either collagen-related peptide (Collagen-related peptide, 0.1 μg/ml) or thrombin (0.04 U/mL) stimulation without altering the expression of P-selectin, glycoprotein Ibα, GPVI, or αIIbβ3. In addition, matrine-treated platelets presented significantly decreased spreading on fibrinogen or collagen and clot retraction along with reduced phosphorylation of c-Src. Moreover, matrine administration significantly impaired the in vivo hemostatic function of platelets, arterial and venous thrombus formation. Furthermore, in platelets stimulated with CRP or thrombin, matrine significantly reduced Reactive oxygen species generation, inhibited the phosphorylation level of ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), p38 (Thr180/Tyr182) and AKT (Thr308/Ser473) as well as increased VASP phosphorylation (Ser239) and intracellular cGMP level. In conclusion, matrine inhibits platelet function, arterial and venous thrombosis, possibly involving inhibition of ROS generation, suggesting that matrine might be used as an antiplatelet agent for treating thrombotic or cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: ROS; hemostasis; matrine; platelet; thrombosis.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Gui, Ding, Tong, Ju, Li, Li, Zeng, Xu and Qiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Arthur J. F., Qiao J., Shen Y., Davis A. K., Dunne E., Berndt M. C., et al. (2012). ITAM Receptor-Mediated Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Human Platelets Occurs via Syk-dependent and Syk-independent Pathways. J. Thromb. Haemost. 10, 1133–1141. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04734.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aszodi A., Pfeifer A., Ahmad M., Glauner M., Zhou X. H., Ny L., et al. (1999). The Vasodilator-Stimulated Phosphoprotein (VASP) Is Involved in cGMP- and cAMP-Mediated Inhibition of Agonist-Induced Platelet Aggregation, but Is Dispensable for Smooth Muscle Function. EMBO J. 18, 37–48. 10.1093/emboj/18.1.37 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

