Parental Reports of Preschoolers' Lexical and Syntactic Development: Validation of the CDI-III for European Portuguese
- PMID: 34366995
- PMCID: PMC8344901
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.677575
Parental Reports of Preschoolers' Lexical and Syntactic Development: Validation of the CDI-III for European Portuguese
Abstract
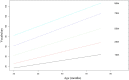
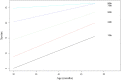
This study presents the validation analysis of the European Portuguese version of the MacArthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventory III (CDI-III-PT). The CDI-III-PT is a parental report measure allowing researchers to assess expressive vocabulary and the syntactic abilities of children aged 2;6-4;0. In this study, we present a version comprising a lexical subscale which follows the Swedish adaptation and an original syntactic subscale allowing us to include language-specific structures. The reports of 739 children were collected; in addition, a standardized measure of language was also administered to a sub-sample of these children and the reports of preschool teachers were collected for another sub-sample. The results indicate a high internal consistency of the lexical and syntactic subscales. As for sociodemographic variables often found to be predictors of language development, as measured by this type of instrument, the results indicate that age and maternal education are significant predictors of the scores, and that first-born children attain higher scores in vocabulary than later born children, but no significant gender differences were found. The scores of the CDI-III-PT are positively correlated with the ones obtained in the standardized language measure, thus supporting their validity. A high agreement between the reports of parents and teachers was also found. These findings indicate that the CDI-III-PT has adequate psychometric properties and that it can be a useful tool for research and clinical practice. The age-based norms that are now provided can be used to evaluate whether a child is performing poorly compared to their peers.
Keywords: European Portuguese; MacArthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventory; syntax; validation; vocabulary.
Copyright © 2021 Cadime, Santos, Ribeiro and Viana.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and norming of the Hungarian CDI-III: A screening tool for language delay.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022 Mar;57(2):252-273. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12686. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022. PMID: 34997807 Free PMC article.
-
Language Development Between 30 and 48 Months in Monolingual Slovenian-Speaking Children: A Study Using the Slovenian Adaptation of the Macarthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventory CDI-III.J Child Lang. 2025 Mar 27:1-17. doi: 10.1017/S0305000925000121. Online ahead of print. J Child Lang. 2025. PMID: 40143758
-
Adaptation of the MacArthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventories for Spanish Children With Down Syndrome: Validity and Reliability Data for Vocabulary.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2016 Aug 1;25(3):371-80. doi: 10.1044/2015_AJSLP-15-0007. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27387223
-
Insufficient evidence for the validity of the Language Development Survey and the MacArthur-Bates Communicative Development Inventories as screening tools: A critical review.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 Mar;58(2):555-575. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12800. Epub 2022 Nov 12. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36370048 Review.
-
How to Build a Communicative Development Inventory: Insights From 43 Adaptations.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2023 Jun 20;66(6):2095-2117. doi: 10.1044/2023_JSLHR-22-00591. Epub 2023 May 17. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2023. PMID: 37195745 Review.
Cited by
-
Early predictors of reading success in first grade.Front Psychol. 2023 Aug 14;14:1140823. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1140823. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37645070 Free PMC article.
-
Parental reports on language development in toddlers and preschoolers based on the Croatian version of Communicative Development Inventories III.Front Psychol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1188550. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1188550. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37546459 Free PMC article.
-
How the communicative development inventories can contribute to clinical assessments of children with speech and language disorders.Front Psychol. 2023 Jul 14;14:1176028. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1176028. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37519399 Free PMC article.
-
How congruent are parent reports on 3-4-year-old children's language skills with other sources of data?Front Psychol. 2023 Jul 28;14:1179999. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1179999. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37575418 Free PMC article.
-
Development and norming of the Hungarian CDI-III: A screening tool for language delay.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022 Mar;57(2):252-273. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12686. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2022. PMID: 34997807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agostinho C., Santos A. L., Duarte I. (2018). The acquisition of Control in European Portuguese, in Complement Clauses in Portuguese: Adult Syntax and Acquisition, eds Santos A. L., Gonçalves A. (London: John Benjamins; ), 263–293.
-
- Altinkaynak S. Ö. (2019). Investigation of the relationship between parental attitudes and children's receptive and expressive language skills. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 7, 892–903. 10.13189/ujer.2019.070331 - DOI
-
- American Educational Research Association (AERA), American Psychological Association, and National Council on Measurement in Education (1999). Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing. Washington, DC: AERA.
-
- Andonova E. (2015). Parental report evidence for toddlers' grammar and vocabulary in Bulgarian. First Lang. 35, 126–136. 10.1177/0142723715574399 - DOI
-
- Bauer D. J., Goldfield B. A., Reznick J. S. (2002). Alternative approaches to analyzing individual differences in the rate of early vocabulary development. Appl. Psycholinguist. 23, 313–335. 10.1017/S0142716402003016 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials