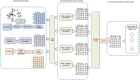
An Ensemble Matrix Completion Model for Predicting Potential Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34367094
- PMCID: PMC8334363
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.694534
An Ensemble Matrix Completion Model for Predicting Potential Drugs Against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
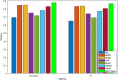
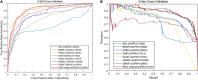
Because of the catastrophic outbreak of global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and its strong infectivity and possible persistence, computational repurposing of existing approved drugs will be a promising strategy that facilitates rapid clinical treatment decisions and provides reasonable justification for subsequent clinical trials and regulatory reviews. Since the effects of a small number of conditionally marketed vaccines need further clinical observation, there is still an urgent need to quickly and effectively repurpose potentially available drugs before the next disease peak. In this work, we have manually collected a set of experimentally confirmed virus-drug associations through the publicly published database and literature, consisting of 175 drugs and 95 viruses, as well as 933 virus-drug associations. Then, because the samples are extremely sparse and unbalanced, negative samples cannot be easily obtained. We have developed an ensemble model, EMC-Voting, based on matrix completion and weighted soft voting, a semi-supervised machine learning model for computational drug repurposing. Finally, we have evaluated the prediction performance of EMC-Voting by fivefold crossing-validation and compared it with other baseline classifiers and prediction models. The case study for the virus SARS-COV-2 included in the dataset demonstrates that our model achieves the outperforming AUPR value of 0.934 in virus-drug association's prediction.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; computational drug repurposing; matrix completion; virus-drug association prediction; weighted voting ensemble model.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Wang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A review of SARS-CoV-2 drug repurposing: databases and machine learning models.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1182465. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1182465. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37601065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Weighted hypergraph learning and adaptive inductive matrix completion for SARS-CoV-2 drug repositioning.Methods. 2023 Nov;219:102-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2023.10.002. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Methods. 2023. PMID: 37804962
-
A computational approach to aid clinicians in selecting anti-viral drugs for COVID-19 trials.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 27;11(1):9047. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88153-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33907209 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning method for repurposing antiviral drugs against new viruses via multi-view nonnegative matrix factorization and its application to SARS-CoV-2.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Jan 17;23(1):bbab526. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab526. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 34965582
-
Molecular Insights of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Molecular Treatments.Curr Mol Med. 2022;22(7):621-639. doi: 10.2174/1566524021666211013121831. Curr Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34645374 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction of disease-related miRNAs by voting with multiple classifiers.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Apr 30;24(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05308-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37122001 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithms for tackling optimization problems across disciplines.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 24;14(1):9403. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56670-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38658593 Free PMC article.
-
A review of SARS-CoV-2 drug repurposing: databases and machine learning models.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 4;14:1182465. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1182465. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37601065 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cai J., Luo J., Wang S., Yang S. (2018). Feature selection in machine learning: a new perspective. Neurocomputing 300 70–79. 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.11.077 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous