Assembling the Current Pieces: The Puzzle of RNA-Mediated Regulation in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 34367109
- PMCID: PMC8334554
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.706690
Assembling the Current Pieces: The Puzzle of RNA-Mediated Regulation in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
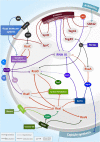
The success of the major opportunistic human Staphylococcus aureus relies on the production of numerous virulence factors, which allow rapid colonization and dissemination in any tissues. Indeed, regulation of its virulence is multifactorial, and based on the production of transcriptional factors, two-component systems (TCS) and small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs). Advances in high-throughput sequencing technologies have unveiled the existence of hundreds of potential RNAs with regulatory functions, but only a fraction of which have been validated in vivo. These discoveries have modified our thinking and understanding of bacterial physiology and virulence fitness by placing sRNAs, alongside transcriptional regulators, at the center of complex and intertwined regulatory networks that allow S. aureus to rapidly adapt to the environmental cues present at infection sites. In this review, we describe the recently acquired knowledge of characterized regulatory RNAs in S. aureus that are associated with metal starvation, nutrient availability, stress responses and virulence. These findings highlight the importance of sRNAs for the comprehension of S. aureus infection processes while raising questions about the interplay between these key regulators and the pathways they control.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; interconnected network; metabolism; regulatory RNA; virulence.
Copyright © 2021 Barrientos, Mercier, Lalaouna and Caldelari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thirty Years of sRNA-Mediated Regulation in Staphylococcus aureus: From Initial Discoveries to In Vivo Biological Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 1;23(13):7346. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137346. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Small RNA Teg41 Regulates Expression of the Alpha Phenol-Soluble Modulins and Is Required for Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2019 Feb 5;10(1):e02484-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02484-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30723124 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental Plasticity of the RNA Content of Staphylococcus aureus Extracellular Vesicles.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 11;12:634226. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.634226. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33776967 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems in Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Regulation.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;409:145-198. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_5019. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 26728068 Review.
-
Current knowledge on regulatory RNAs and their machineries in Staphylococcus aureus.RNA Biol. 2012 Apr;9(4):402-13. doi: 10.4161/rna.20103. Epub 2012 Apr 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22546940 Review.
Cited by
-
Thirty Years of sRNA-Mediated Regulation in Staphylococcus aureus: From Initial Discoveries to In Vivo Biological Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 1;23(13):7346. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137346. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SSR42 is a novel regulator of cytolytic activity in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2025 Jun 11;16(6):e0077225. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00772-25. Epub 2025 May 9. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40340377 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome Profiling Methods Adapted to the Study of RNA-Dependent Translation Regulation in Staphylococcus aureus.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2741:73-100. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3565-0_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38217649
-
CodY controls the SaeR/S two-component system by modulating branched-chain fatty acid synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2024 Nov 21;206(11):e0019124. doi: 10.1128/jb.00191-24. Epub 2024 Oct 9. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 39382300 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neutrophil myeloperoxidase inhibitor SPIN by the small RNA Teg49 in Staphylococcus aureus.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Jun;117(6):1447-1463. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14919. Epub 2022 May 31. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35578788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Qatouseh L. F., Chinni S. V., Seggewiss J., Proctor R. A., Brosius J., Rozhdestvensky T. S., et al. (2010). Identification of differentially expressed small non-protein-coding RNAs in Staphylococcus aureus displaying both the normal and the small-colony variant phenotype. J. Mol. Med. (Berl) 88 565–575. 10.1007/s00109-010-0597-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anderson K. L., Roberts C., Disz T., Vonstein V., Hwang K., Overbeek R., et al. (2006). Characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus heat shock, cold shock, stringent, and SOS responses and their effects on log-phase mRNA turnover. J. Bacteriol. 188 6739–6756. 10.1128/jb.00609-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beaume M., Hernandez D., Farinelli L., Deluen C., Linder P., Gaspin C., et al. (2010). Cartography of methicillin-resistant S. aureus transcripts: detection, orientation and temporal expression during growth phase and stress conditions. PLoS One 5:e10725. 10.1371/journal.pone.0010725 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

