Trichoderma: A Treasure House of Structurally Diverse Secondary Metabolites With Medicinal Importance
- PMID: 34367122
- PMCID: PMC8342961
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.723828
Trichoderma: A Treasure House of Structurally Diverse Secondary Metabolites With Medicinal Importance
Abstract
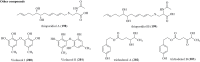
Fungi play an irreplaceable role in drug discovery in the course of human history, as they possess unique abilities to synthesize diverse specialized metabolites with significant medicinal potential. Trichoderma are well-studied filamentous fungi generally observed in nature, which are widely marketed as biocontrol agents. The secondary metabolites produced by Trichoderma have gained extensive attention since they possess attractive chemical structures with remarkable biological activities. A large number of metabolites have been isolated from Trichoderma species in recent years. A previous review by Reino et al. summarized 186 compounds isolated from Trichoderma as well as their biological activities up to 2008. To update the relevant list of reviews of secondary metabolites produced from Trichoderma sp., we provide a comprehensive overview in regard to the newly described metabolites of Trichoderma from the beginning of 2009 to the end of 2020, with emphasis on their chemistry and various bioactivities. A total of 203 compounds with considerable bioactivities are included in this review, which is worth expecting for the discovery of new drug leads and agrochemicals in the foreseeable future. Moreover, new strategies for discovering secondary metabolites of Trichoderma in recent years are also discussed herein.
Keywords: Trichoderma; bioactive compounds; biological activity; chemical diversity; secondary metabolites.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Tang, Huang, Li, Wei, Jiang, Liu, Yu, Zhu, Chen and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- Bhardwaj N., Kumar J. (2017). Characterization of volatile secondary metabolites from Trichoderma asperellum. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 9 954–959. 10.31018/jans.v9i2.1303 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

