Sex Matters: Physiological Abundance of Immuno-Regulatory CD71+ Erythroid Cells Impair Immunity in Females
- PMID: 34367164
- PMCID: PMC8334724
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.705197
Sex Matters: Physiological Abundance of Immuno-Regulatory CD71+ Erythroid Cells Impair Immunity in Females
Abstract
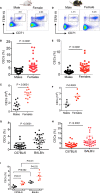
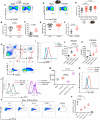
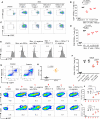
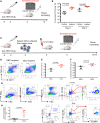
Mature erythrocytes are the major metabolic regulators by transporting oxygen throughout the body. However, their precursors and progenitors defined as CD71+ Erythroid Cells (CECs) exhibit a wide range of immunomodulatory properties. Here, we uncover pronounced sexual dimorphism in CECs. We found female but not male mice, both BALB/c and C57BL/6, and human females were enriched with CECs. CECs, mainly their progenitors defined as CD45+CECs expressed higher levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), PDL-1, VISTA, Arginase II and Arginase I compared to their CD45- counterparts. Consequently, CECs by the depletion of L-arginine suppress T cell activation and proliferation. Expansion of CECs in anemic mice and also post-menstrual cycle in women can result in L-arginine depletion in different microenvironments in vivo (e.g. spleen) resulting in T cell suppression. As proof of concept, we found that anemic female mice and mice adoptively transferred with CECs from anemic mice became more susceptible to Bordetella pertussis infection. These observations highlight the role of sex and anemia-mediated immune suppression in females. Notably, enriched CD45+CECs may explain their higher immunosuppressive properties in female BALB/c mice. Finally, we observed significantly more splenic central macrophages in female mice, which can explain greater extramedullary erythropoiesis and subsequently abundance of CECs in the periphery. Thus, sex-specific differences frequency in the frequency of CECs might be imprinted by differential erythropoiesis niches and hormone-dependent manner.
Keywords: CD71+ erythroid cells; anemia and immunity; anemia and infection; females; immune system and sex.
Copyright © 2021 Mashhouri, Koleva, Huynh, Okoye, Shahbaz and Elahi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

