An Early Myelosuppression in the Acute Mouse Sepsis Is Partly Outcome-Dependent
- PMID: 34367170
- PMCID: PMC8339578
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.708670
An Early Myelosuppression in the Acute Mouse Sepsis Is Partly Outcome-Dependent
Abstract
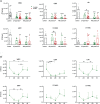
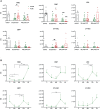
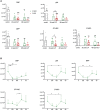
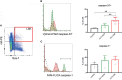
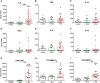
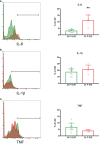
Adult hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) respond to bacterial infections by expansion to myeloid cells. Sepsis impairs this process by suppressing differentiation of stem cells subsequently contributing to an ineffective immune response. Whether the magnitude of HSPCs impairment in sepsis is severity-dependent remains unknown. This study investigated dynamics of the HSPC immune-inflammatory response in the bone marrow, splenic, and blood compartments in moribund and surviving septic mice. The 12-week-old outbred CD-1 female mice (n=65) were subjected to a cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) sepsis, treated with antibiotics and fluid resuscitation, and stratified into predicted-to-die (P-DIE) and predicted-to-survive (P-SUR) cohorts for analysis. CLP strongly reduced the common myeloid and multipotent progenitors, short- and long-term hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) counts in the bone marrow; lineage-ckit+Sca-1+ and short-term HSC suppression was greater in P-DIE versus P-SUR mice. A profound depletion of the common myeloid progenitors occurred in the blood (by 75%) and spleen (by 77%) of P-DIE. In P-SUR, most common circulating HSPCs subpopulations recovered to baseline by 72 h post-CLP. Analysis of activated caspase-1/-3/-7 revealed an increased apoptotic (by 30%) but not pyroptotic signaling in the bone marrow HSCs of P-DIE mice. The bone marrow from P-DIE mice revealed spikes of IL-6 (by 5-fold), CXCL1/KC (15-fold), CCL3/MIP-1α (1.7-fold), and CCL2/MCP-1 (2.8-fold) versus P-SUR and control (TNF, IFN-γ, IL-1β, -5, -10 remained unaltered). Summarizing, our findings demonstrate that an early sepsis-induced impairment of myelopoiesis is strongly outcome-dependent but varies among compartments. It is suggestive that the HSCPC loss is at least partly due to an increased apoptosis but not pyroptosis.
Keywords: caspases; cecal ligation and puncture; hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells; immunity; infection; outcome prediction.
Copyright © 2021 Skirecki, Drechsler, Jeznach, Hoser, Jafarmadar, Kawiak and Osuchowski.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Survivors of polymicrobial sepsis are refractory to G-CSF-induced emergency myelopoiesis and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell mobilization.Stem Cell Reports. 2024 May 14;19(5):639-653. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.03.007. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Stem Cell Reports. 2024. PMID: 38608679 Free PMC article.
-
Early severe impairment of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from the bone marrow caused by CLP sepsis and endotoxemia in a humanized mice model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015 Aug 14;6(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0135-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26272069 Free PMC article.
-
The Fluctuations of Leukocytes and Circulating Cytokines in Septic Humanized Mice Vary With Outcome.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1427. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01427. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31297113 Free PMC article.
-
The Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cell Response to Hemorrhage, Injury, and Sepsis: A Review of Pathophysiology.Shock. 2021 Jul 1;56(1):30-41. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001699. Shock. 2021. PMID: 33234838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myelopoiesis in the Context of Innate Immunity.J Innate Immun. 2018;10(5-6):365-372. doi: 10.1159/000489406. Epub 2018 Jun 6. J Innate Immun. 2018. PMID: 29874678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Active cytomegalovirus infection in mechanically ventilated patients with sepsis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):1405. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10304-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39696007 Free PMC article.
-
Metamizole outperforms meloxicam in sepsis: insights on analgesics, survival and immunomodulation in the peritoneal contamination and infection sepsis model.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1432307. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1432307. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39281680 Free PMC article.
-
Survivors of polymicrobial sepsis are refractory to G-CSF-induced emergency myelopoiesis and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell mobilization.Stem Cell Reports. 2024 May 14;19(5):639-653. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.03.007. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Stem Cell Reports. 2024. PMID: 38608679 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus end-organ disease in immunocompromised critically ill patients: key concerns demanding attention.Crit Care. 2024 Sep 10;28(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05070-3. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39256773 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The role of inflammation in hematopoiesis and bone marrow failure: What can we learn from mouse models?Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 11;13:951937. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951937. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

