The Salivary Microbiota of Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis Is Distinctive and Pathogenic
- PMID: 34367180
- PMCID: PMC8335641
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.713647
The Salivary Microbiota of Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis Is Distinctive and Pathogenic
Abstract
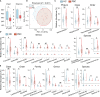
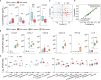
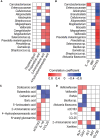
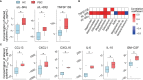
The role of host-microbiota interactions in primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) has received increased attention. However, the impact of PBC on the oral microbiota and contribution of the oral microbiota to PBC are unclear. In this study, thirty-nine PBC patients without other diseases and 37 healthy controls (HCs) were enrolled and tested for liver functions and haematological variables. Saliva specimens were collected before and after brushing, microbiota was determined using 16S rDNA sequencing, metabolomics was profiled using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer (GC-MS), 80 cytokines were assayed using biochips, and inflammation inducibility was evaluated using OKF6 keratinocytes and THP-1 macrophages. Finally, the effect of ultrasonic scaling on PBC was estimated. Compared with HCs, PBC saliva had enriched taxa such as Bacteroidetes, Campylobacter, Prevotella and Veillonella and depleted taxa such as Enterococcaceae, Granulicatella, Rothia and Streptococcus. PBC saliva also had enriched sCD163, enriched metabolites such as 2-aminomalonic acid and 1-dodecanol, and depleted metabolites such as dodecanoic acid and propylene glycol. sCD163, 4-hydroxybenzeneacetic acid and 2-aminomalonic acid were significantly correlated with salivary cytokines, bacteria and metabolites. Salivary Veillonellaceae members, 2-aminomalonic acid, and sCD163 were positively correlated with liver function indicators such as serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT). PBC salivary microbes induced more soluble interleukin (IL)-6 receptor α (sIL-6Rα), sIL-6Rβ and tumour necrosis factor ligand superfamily (TNFSF)13B from OKF6 keratinocytes, and PBC salivary supernatant induced more IL-6, IL-10, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), chemokine (C-C motif) ligand (CCL)13, C-X-C motif chemokine (CXC)L1 and CXCL16 from THP-1 macrophages. Toothbrushing significantly reduced the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α and harmful metabolites such as cadaverine and putrescine in PBC but not HC saliva after P-value correction. The levels of ALP and bilirubin in PBC serum were decreased after ultrasonic scaling. Together, PBC patients show significant alterations in their salivary microbiota, likely representing one cause and treatment target of oral inflammation and worsening liver functions.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; immunity; liver; metabolites; microbiota.
Copyright © 2021 Lv, Jiang, Chen, Wang, Wang, Ye, Li, Fang, Lu, Yang, Gu, Chen, Diao, Yan and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dysbiosis of oral microbiota and its association with salivary immunological biomarkers in autoimmune liver disease.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 3;13(7):e0198757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198757. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29969462 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Salivary Microbiota and Its Association With Host Inflammatory Mediators in Periodontitis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Jun 21;9:216. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00216. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31281801 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Serum and Fecal Bile Acid Profiles and Interaction with Gut Microbiota in Primary Biliary Cholangitis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020 Feb;58(1):25-38. doi: 10.1007/s12016-019-08731-2. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 30900136
-
Therapeutic trials of biologics in primary biliary cholangitis: An open label study of abatacept and review of the literature.J Autoimmun. 2019 Jul;101:26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 24. J Autoimmun. 2019. PMID: 31027870 Review.
-
Mig chemokine in primary biliary cirrhosis.Clin Ter. 2019 May-Jun;170(3):e211-e215. doi: 10.7417/CT.2019.2135. Clin Ter. 2019. PMID: 31173052 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbiota of Saliva: A Non-invasive Diagnostic Tool.Indian J Microbiol. 2024 Jun;64(2):328-342. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01219-4. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Indian J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39010986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary biliary cholangitis: a summary of pathogenesis and therapies.Ann Gastroenterol. 2025 Mar-Apr;38(2):121-132. doi: 10.20524/aog.2025.0953. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Ann Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40124425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Probiotics on Liver Diseases: Current In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jun;17(3):1688-1710. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10431-z. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39739162 Review.
-
Alterations of oral microbiota are associated with the development and severity of acute pancreatitis.J Oral Microbiol. 2023 Oct 5;15(1):2264619. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2023.2264619. eCollection 2023. J Oral Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37808891 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic Combination CBLEB Alleviates Streptococcus pneumoniae Infection Through Immune Regulation in Immunocompromised Rats.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Feb 15;15:987-1004. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S348047. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35210807 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

