Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells as a New Therapeutic Target for Autoimmune Pancreatitis and IgG4-Related Disease
- PMID: 34367181
- PMCID: PMC8342887
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.713779
Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells as a New Therapeutic Target for Autoimmune Pancreatitis and IgG4-Related Disease
Abstract
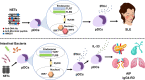
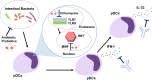
Although plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) able to produce large amounts of type 1 interferons (IFN-I) play beneficial roles in host defense against viral infections, excessive activation of pDCs, followed by robust production of IFN-I, causes autoimmune disorders including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and psoriasis. Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), which is recognized as a pancreatic manifestation of systemic immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD), is a chronic fibroinflammatory disorder driven by autoimmunity. IgG4-RD is a multi-organ autoimmune disorder characterized by elevated serum concentrations of IgG4 antibody and infiltration of IgG4-expressing plasmacytes in the affected organs. Although the immunopathogenesis of IgG4-RD and AIP has been poorly elucidated, recently, we found that activation of pDCs mediates the development of murine experimental AIP and human AIP/IgG4-RD via the production of IFN-I and interleukin-33 (IL-33). Depletion of pDCs or neutralization of signaling pathways mediated by IFN-I and IL-33 efficiently inhibited the development of experimental AIP. Furthermore, enhanced expression of IFN-I and IL-33 was observed in the pancreas and serum of human AIP/IgG4-RD. Thus, AIP and IgG4-RD share their immunopathogenesis with SLE and psoriasis because in all these conditions, IFN-I production by pDCs contributes to the pathogenesis. Because the enhanced production of IFN-I and IL-33 by pDCs promotes chronic inflammation and fibrosis characteristic for AIP and IgG4-RD, neutralization of IFN-I and IL-33 could be a new therapeutic option for these disorders. In this Mini Review, we discuss the pathogenic roles played by the pDC-IFN-I-IL-33 axis and the development of a new treatment targeting this axis in AIP and IgG4-RD.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease; autoimmune pancreatitis; interferon-I; interleukin-33; plasmacytoid dendritic cells.
Copyright © 2021 Minaga, Watanabe, Hara, Yoshikawa, Kamata and Kudo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

