Janus Kinase Inhibition Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Injury and Neuroinflammation Through Reducing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition
- PMID: 34367186
- PMCID: PMC8339584
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.714943
Janus Kinase Inhibition Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Injury and Neuroinflammation Through Reducing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory responses play a multiphase role in the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemic stroke (IS). Ruxolitinib (Rux), a selective oral JAK 1/2 inhibitor, reduces inflammatory responses via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Based on its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, we hypothesized that it may have a protective effect against stroke. The aim of this study was to investigate whether inhibition of JAK2 has a neuroprotective effect on ischemic stroke and to explore the potential molecular mechanisms.
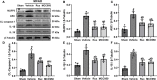
Methods: Rux, MCC950 or vehicle was applied to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice in vivo and an oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) model in vitro. After 3 days of reperfusion, neurological deficit scores, infarct volume and brain water content were assessed. Immunofluorescence staining and western blots were used to measure the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome components. The infiltrating cells were investigated by flow cytometry. Proinflammatory cytokines were assessed by RT-qPCR. The expression of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway was measured by western blots. Local STAT3 deficiency in brain tissue was established with a lentiviral vector carrying STAT3 shRNA, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were used to investigate the interplay between NLRP3 and STAT3 signaling.
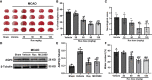
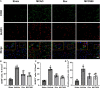
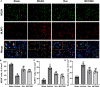
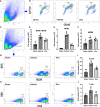
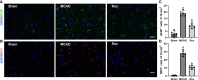
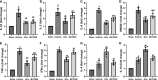
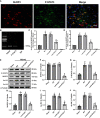
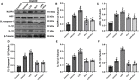
Results: Rux treatment improved neurological scores, decreased the infarct size and ameliorated cerebral edema 3 days after stroke. In addition, immunofluorescence staining and western blots showed that Rux application inhibited the expression of proteins related to the NLRP3 inflammasome and phosphorylated STAT3 (P-STAT3) in neurons and microglia/macrophages. Furthermore, Rux administration inhibited the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IFN-γ, HMGB1, IL-1β, IL-2, and IL-6, suggesting that Rux may alleviate IS injury by inhibiting proinflammatory reactions via JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway regulation. Infiltrating macrophages, B, T, cells were also reduced by Rux. Local STAT3 deficiency in brain tissue decreased histone H3 and H4 acetylation on the NLRP3 promoter and NLRP3 inflammasome component expression, indicating that the NLRP3 inflammasome may be directly regulated by STAT3 signaling. Rux application suppressed lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced NLRP3 inflammasome secretion and JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation in the OGD/R model in vitro.
Conclusion: JAK2 inhibition by Rux in MCAO mice decreased STAT3 phosphorylation, thus inhibiting the expression of downstream proinflammatory cytokines and the acetylation of histones H3 and H4 on the NLRP3 promoter, resulting in the downregulation of NLRP3 inflammasome expression.
Keywords: JAK2/STAT3; NLRP3 inflammasome; ischemic stroke; neuroinflammation; ruxolitinib.
Copyright © 2021 Zhu, Jian, Zhong, Ye, Zhang, Hu, Pu, Gu and Xiong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
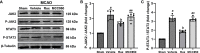
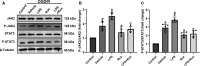
References
-
- Guekht A, Skoog I, Edmundson S, Zakharov V, Korczyn AD. Artemida Trial (a Randomized Trial of Efficacy, 12 Months International Double-Blind Actovegin): A Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess the Efficacy of Actovegin in Poststroke Cognitive Impairment. Stroke (2017) 48(5):1262–70. 10.1161/strokeaha.116.014321 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

