Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and the Risk of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
- PMID: 34367246
- PMCID: PMC8339995
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.688849
Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and the Risk of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
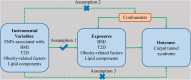
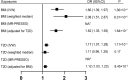
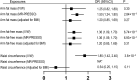
Some previous observational studies have reported an increased risk of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) in patients with obesity or type 2 diabetes (T2D), which was however, not observed in some other studies. In this study we performed a two-sample Mendelian randomization to assess the causal effect of obesity, T2D on the risk of CTS. Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with the body mass index (BMI) and T2D were extracted from genome-wide association studies. Summary-level results of CTS were available through FinnGen repository. Univariable Mendelian randomization (MR) with inverse-variance-weighted method indicated a positive correlation of BMI with CTS risk [odds ratio (OR) 1.66, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.39-1.97]. Genetically proxied T2D also significantly increased the risk of CTS [OR 1.17, 95% CI (1.07-1.29)]. The causal effect of BMI and T2D on CTS remained consistent after adjusting for each other with multivariable MR. Our mediation analysis indicated that 34.4% of BMI's effect of CTS was mediated by T2D. We also assessed the effects of several BMI and glycemic related traits on CTS. Waist circumference and arm fat-free mass were also causally associated with CTS. However, the associations disappeared after adjusting for the effect of BMI. Our findings indicate that obesity and T2D are independent risk factors of CTS.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; body mass index; carpal tunnel syndrome; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2021 Mi and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

