Study on the Regulation Effect of Optogenetic Technology on LFP of the Basal Ganglia Nucleus in Rotenone-Treated Rats
- PMID: 34367273
- PMCID: PMC8342173
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9938566
Study on the Regulation Effect of Optogenetic Technology on LFP of the Basal Ganglia Nucleus in Rotenone-Treated Rats
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurological degenerative disease that cannot be completely cured, although drugs can improve or alleviate its symptoms. Optogenetic technology, which stimulates or inhibits neurons with excellent spatial and temporal resolution, provides a new idea and approach for the precise treatment of Parkinson's disease. However, the neural mechanism of photogenetic regulation remains unclear.
Objective: In this paper, we want to study the nonlinear features of EEG signals in the striatum and globus pallidus through optogenetic stimulation of the substantia nigra compact part.
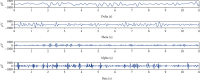
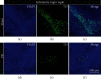
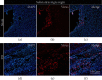
Methods: Rotenone was injected stereotactically into the substantia nigra compact area and ventral tegmental area of SD rats to construct rotenone-treated rats. Then, for the optogenetic manipulation, we injected adeno-associated virus expressing channelrhodopsin to stimulate the globus pallidus and the striatum with a 1 mW blue light and collected LFP signals before, during, and after light stimulation. Finally, the collected LFP signals were analyzed by using nonlinear dynamic algorithms.
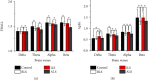
Results: After observing the behavior and brain morphology, 16 models were finally determined to be successful. LFP results showed that approximate entropy and fractal dimension of rats in the control group were significantly greater than those in the experimental group after light treatment (p < 0.05). The LFP nonlinear features in the globus pallidus and striatum of rotenone-treated rats showed significant statistical differences before and after light stimulation (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Optogenetic technology can regulate the characteristic value of LFP signals in rotenone-treated rats to a certain extent. Approximate entropy and fractal dimension algorithm can be used as an effective index to study LFP changes in rotenone-treated rats.
Copyright © 2021 Zongya Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Frequency-Specific Optogenetic Deep Brain Stimulation of Subthalamic Nucleus Improves Parkinsonian Motor Behaviors.J Neurosci. 2020 May 27;40(22):4323-4334. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3071-19.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 20. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32312888 Free PMC article.
-
Acute intranigral infusion of rotenone in rats causes progressive biochemical lesions in the striatum similar to Parkinson's disease.Brain Res. 2005 Jul 12;1049(2):147-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.04.051. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15936733
-
Systematic administration of iptakalim, an ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener, prevents rotenone-induced motor and neurochemical alterations in rats.J Neurosci Res. 2005 May 1;80(3):442-9. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20467. J Neurosci Res. 2005. PMID: 15795934
-
Substantia nigra control of basal ganglia nuclei.J Neural Transm Suppl. 2009;(73):91-101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-92660-4_7. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2009. PMID: 20411770 Review.
-
Neurotransmitters in the basal ganglia.Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;11(1 Suppl):89-99. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100046217. Can J Neurol Sci. 1984. PMID: 6143612 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

