Novel Compound Q-1 Alleviates Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats through the NF- κ B Pathway
- PMID: 34367306
- PMCID: PMC8339345
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6627290
Novel Compound Q-1 Alleviates Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats through the NF- κ B Pathway
Abstract
Background: Q-1 is a novel compound extracted from the Miao medicine Tiekuaizi. Although Q-1 is known to be a coumarin derivative, its structure has not been deposited in the ACX library. Our previous study showed that Q-1 inhibits the activity of inflammatory cells. This study explores the efficacy of Q-1 in regulating rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The findings show that Q-1 acts through the NF-κB signaling pathway.
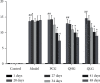
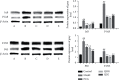
Methods: The effects of Q-1 were explored using a bovine type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rat model. The CIA rats were intragastrically administered with high (30 mg·kg-1) or low (15 mg·kg-1) doses of Q-1. The control group was administered with an equal volume of drinking water, while the positive control group was administered with Tripterygium glycoside (9.45 mg·kg-1) for 28 consecutive days. The arthritis indices and ankle joint swelling rates were determined. The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) in serum and sialic acid (SA) in liver homogenate were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The pathological features of the ankle joint were analyzed by hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. The IκB, P-IκB, P65, and P-P65 protein levels in synovial tissue were assayed by western blotting.
Results: The arthritis index, ankle joint swelling rate, IL-1β, IL-6, and MCP-1 levels in serum, SA level in liver tissue, and IκB, P-IκB, P65, and P-P65 protein levels in synovial tissues were significantly higher (P < 0.01) in the CIA model compared to the control group. RA was successfully replicated by the CIA model, as shown by the joint swelling results and histopathological sections of the ankle. Notably, all the above indicators decreased significantly (P < 0.01) after treatment with Q-1 compared to the model. In addition, animals treated with Q-1 showed lower inflammation in the ankle joints than the model rats.
Conclusion: The findings indicate that Q-1 effectively inhibited RA in rats by downregulating IκB, P-IκB, P65, and P-P65, inhibiting the excessive release of inflammatory factors, and inhibiting the overactivation of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2021 Ting Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

