A Review of 3D Printing in Dentistry: Technologies, Affecting Factors, and Applications
- PMID: 34367410
- PMCID: PMC8313360
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9950131
A Review of 3D Printing in Dentistry: Technologies, Affecting Factors, and Applications
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) printing technologies are advanced manufacturing technologies based on computer-aided design digital models to create personalized 3D objects automatically. They have been widely used in the industry, design, engineering, and manufacturing fields for nearly 30 years. Three-dimensional printing has many advantages in process engineering, with applications in dentistry ranging from the field of prosthodontics, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and oral implantology to orthodontics, endodontics, and periodontology. This review provides a practical and scientific overview of 3D printing technologies. First, it introduces current 3D printing technologies, including powder bed fusion, photopolymerization molding, and fused deposition modeling. Additionally, it introduces various factors affecting 3D printing metrics, such as mechanical properties and accuracy. The final section presents a summary of the clinical applications of 3D printing in dentistry, including manufacturing working models and main applications in the fields of prosthodontics, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and oral implantology. The 3D printing technologies have the advantages of high material utilization and the ability to manufacture a single complex geometry; nevertheless, they have the disadvantages of high cost and time-consuming postprocessing. The development of new materials and technologies will be the future trend of 3D printing in dentistry, and there is no denying that 3D printing will have a bright future.
Copyright © 2021 Yueyi Tian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no financial or personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work.
Figures
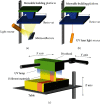

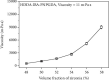
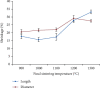



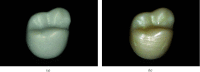
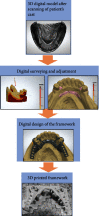

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
