Spirulina platensis Consumption Prevents Obesity and Improves the Deleterious Effects on Intestinal Reactivity in Rats Fed a Hypercaloric Diet
- PMID: 34367461
- PMCID: PMC8337120
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3260789
Spirulina platensis Consumption Prevents Obesity and Improves the Deleterious Effects on Intestinal Reactivity in Rats Fed a Hypercaloric Diet
Abstract
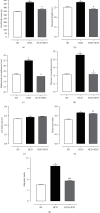
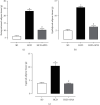
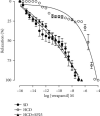
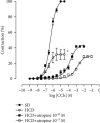
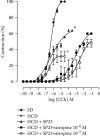
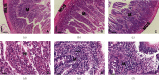
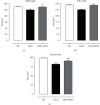
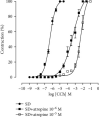
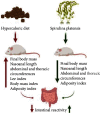
The consumption of hypercaloric diets is related to the development of obesity, favoring the etiology of gastrointestinal disorders. In this context, Spirulina platensis (SP), some blue-green algae with antioxidant action, appears as a potential therapeutic alternative to prevent obesity and associated intestinal disorders. Thus, the present study is aimed at evaluating the deleterious effects of the hypercaloric diet on the contractile and relaxing reactivity of the ileum of rats, as well as the possible preventive mechanisms of dietary supplementation with SP. Wistar rats were divided into three groups: fed a standard diet (SD), a hypercaloric diet (HCD), and/or supplemented with 25 mg/kg SP (HCD + SP25) for 8 weeks. The hypercaloric diet was effective in promoting obesity in rats, as well as decreasing potency and ileal relaxing and contractile efficacy. In contrast, dietary supplementation with SP was able to prevent some of the parameters of experimental obesity. In addition, SP prevented the reduction of intestinal reactivity, possibly due to a positive modulation of voltage-gated calcium channels (CaV) and negative regulation of muscarinic receptors (M3). Thus, food supplementation with Spirulina platensis becomes a promising alternative in the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases induced and/or aggravated by obesity.
Copyright © 2021 Anderson Fellyp Avelino Diniz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brennan V. M., Kumanyika S. K., Zambrana R. E. Baltimore (MD): Johns Hopkins University Press; 2014. Introduction: advancing a new conversation about obesity in the underserved. Obesity interventions in underserved communities: evidence and directions.
-
- WHO. Health topics–obesity and overweight. WHO; 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

