Atypical Kawasaki Disease in an Adolescent with Multivisceral Involvement
- PMID: 34367708
- PMCID: PMC8337161
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8941847
Atypical Kawasaki Disease in an Adolescent with Multivisceral Involvement
Abstract
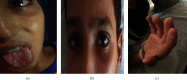
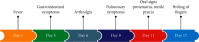
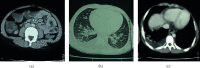
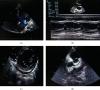
Kawasaki disease (KD) is a vasculitis mostly seen in children aged less than 5 years. It can involve different organs and tissues. Its diagnosis is based on the clinical criteria of the American Heart Association (AHA). We report a case of a Moroccan adolescent with an atypical presentation of KD initially treated as typhoid fever. Gastrointestinal, renal, and pulmonary signs were the main clinical findings that made the diagnosis of KD challenging and delayed. The consequence was a severe cardiac damage with myocarditis and coronary artery dilation. KD is uncommon in adolescents, and it is important to recognize the atypical forms and the different presentations of KD in order to prevent the delay of diagnosis and treatment, and hence the cardiac complications.
Copyright © 2021 Zohair El Haddar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children. Arerugi. 1967;16:178–222. in Japanese. - PubMed
-
- Advani N., Santoso L. A., Sastroasmoro S. Profile of kawasaki disease in adolescents: is it different? Acta Medica Indonesiana. 2019;51(1):42–46. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

