Neck of Femur Fracture in Young Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease and Hyperparathyroidism: A Report of Three Cases and Proposed Treatment Algorithm
- PMID: 34367767
- PMCID: PMC8338123
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.16155
Neck of Femur Fracture in Young Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease and Hyperparathyroidism: A Report of Three Cases and Proposed Treatment Algorithm
Abstract
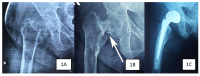
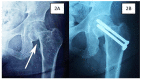
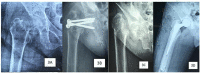
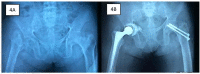
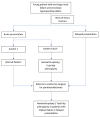
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is a complication arising from untreated end-stage renal disease (ESRD). It can invariably lead to osteoporosis and subsequently cause pathological neck of femur (NOF) fracture. Despite being young, osteosynthesis in neck of femur fractures of these patients often leads to nonunion and implant failure due to severely osteoporotic bone. We present our experience in managing three young patients with ESRD and secondary hyperthyroidism who sustained NOF fractures. All three patients were successfully treated and showed no complication at one year post-operation. Based on our experience and literature review, we propose a simple algorithm to guide the management of these patients.
Keywords: bipolar hemiarthroplasty; end stage renal disease (esrd); hyperparathyroid; neck of femur fracture; pathological fracture; total hip replacement (thr); young adults.
Copyright © 2021, Raj et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Hip fractures in young adults: a retrospective cross-sectional study of characteristics, injury mechanism, risk factors, complications and follow-up. Wang MT, Yao SH, Wong P, et al. Arch Osteoporos. 2017;12:46. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
