Mesh Repair of Rectus Diastasis for Abdominoplasty is Safer than Suture Plication
- PMID: 34367851
- PMCID: PMC8337067
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003721
Mesh Repair of Rectus Diastasis for Abdominoplasty is Safer than Suture Plication
Abstract
Concerns regarding infection, extrusion, and pain have traditionally precluded the use of mesh to treat severe rectus diastasis during abdominoplasty in the United States. We describe a mesh abdominoplasty technique, and we hypothesize that the complication rate using mesh is greater than the complication rate of suture plication.
Methods: Inclusion criteria for mesh abdominoplasty were patients who (1) had retrorectus planar mesh for repair of rectus diastasis, (2) did not have concurrent ventral hernia, and (3) underwent skin tailoring. Patients who underwent rectus plication with suture, and met criteria 2 and 3 above were included in a sample of consecutive standard abdominoplasty patients. The primary endpoint was surgical site occurrence at any time after surgery, as determined with review of their office and hospital medical records. Secondary endpoints included surgical site infection, revision rates, postoperative course, and aesthetics assessed with their last set of office photographs.
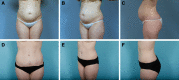
Results: Surgical site occurrence rate was 0% of the 40 patients in the mesh group and 19% of the 37 patients in the standard group (P = 0.005); rates of soft-tissue revision were 23% in the mesh group and 27% in the standard group (P = 0.84). As to aesthetics, the mesh abdominoplasty patients had mean statistically lower preoperative scores in comparison with the standard plication group (65.8 ± 11.6 versus 70.3 ± 11.4, P = 0.0013). The mesh group had a statistical improvement to 75.9 ± 12.6 (P < 0.0001), whereas the standard plication group improved to 82.5 ± 11.4 (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Retrorectus mesh placement in a cohort of patients with severe rectus diastasis had a complication rate lower than that seen in a cohort of patients with less severe rectus diastasis, therefore negating our original hypothesis. This was done without compromising aesthetic improvement.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures



References
-
- ElHawary H, Abdelhamid K, Meng F, et al. . A comprehensive, evidence-based literature review of the surgical treatment of rectus diastasis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;146:1151–1164. - PubMed
-
- Matarasso A, Schneider LF, Barr J. The incidence and management of secondary abdominoplasty and secondary abdominal contour surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133:40–50. - PubMed
-
- Cormenzana PS, Samprón NM, Escudero-Nafs FJ. Secondary abdominoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2008;32:503–508. - PubMed
-
- al-Qattan MM. Abdominoplasty in multiparous women with severe musculoaponeurotic laxity. Br J Plast Surg. 1997;50:450–455. - PubMed
-
- van Uchelen JH, Kon M, Werker PM. The long-term durability of plication of the anterior rectus sheath assessed by ultrasonography. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:1578–1584. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
