Recent Advances in the Development of Theranostic Nanoparticles for Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 34367883
- PMCID: PMC8342263
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.62730
Recent Advances in the Development of Theranostic Nanoparticles for Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
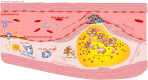
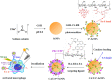
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death worldwide. CVD includes a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels such as myocardial infarction, ischemic heart, ischemic injury, injured arteries, thrombosis and atherosclerosis. Amongst these, atherosclerosis is the dominant cause of CVD and is an inflammatory disease of the blood vessel wall. Diagnosis and treatment of CVD remain the main challenge due to the complexity of their pathophysiology. To overcome the limitations of current treatment and diagnostic techniques, theranostic nanomaterials have emerged. The term "theranostic nanomaterials" refers to a multifunctional agent with both therapeutic and diagnostic abilities. Theranostic nanoparticles can provide imaging contrast for a diversity of techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT). In addition, they can treat CVD using photothermal ablation and/or medication by the drugs in nanoparticles. This review discusses the latest advances in theranostic nanomaterials for the diagnosis and treatment of CVDs according to the order of disease development. MRI, CT, near-infrared spectroscopy (NIR), and fluorescence are the most widely used strategies on theranostics for CVDs detection. Different treatment methods for CVDs based on theranostic nanoparticles have also been discussed. Moreover, current problems of theranostic nanoparticles for CVDs detection and treatment and future research directions are proposed.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cardiovascular diseases; ischemic heart; myocardial infarction; nanomaterials; theranostics; thrombosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Mendis S, Puska P, Norrving B, Organization WH. Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control: WHO; 2011.
-
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N. et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–88. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Afroz R, Cao Y, Rostam MA, Ta H, Xu S, Zheng W. et al. Signalling pathways regulating galactosaminoglycan synthesis and structure in vascular smooth muscle: implications for lipoprotein binding and atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;187:88–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

