COVID-19 patient with an incubation period of 27 d: A case report
- PMID: 34368314
- PMCID: PMC8316961
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i21.5955
COVID-19 patient with an incubation period of 27 d: A case report
Abstract
Background: As a highly contagious disease, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is wreaking havoc around the world due to continuous spread among close contacts mainly via droplets, aerosols, contaminated hands or surfaces. Therefore, centralized isolation of close contacts and suspected patients is an important measure to prevent the transmission of COVID-19. At present, the quarantine duration in most countries is 14 d due to the fact that the incubation period of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is usually identified as 1-14 d with median estimate of 4-7.5 d. Since COVID-19 patients in the incubation period are also contagious, cases with an incubation period of more than 14 d need to be evaluated.
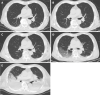
Case summary: A 70-year-old male patient was admitted to the Department of Respiratory Medicine of The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University on April 5 due to a cough with sputum and shortness of breath. On April 10, the patient was transferred to the Fever Clinic for further treatment due to close contact to one confirmed COVID-19 patient in the same room. During the period from April 10 to May 6, nucleic acid and antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 were tested 7 and 4 times, respectively, all of which were negative. On May 7, the patient developed fever with a maximum temperature of 39℃, and his respiratory difficulties had deteriorated. The results of nucleic acid and antibody detection of SARS-CoV-2 were positive. On May 8, the nucleic acid and antibody detection of SARS-CoV-2 by Heilongjiang Provincial Center for Disease Control were also positive, and the patient was diagnosed with COVID-19 and reported to the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Conclusion: This case highlights the importance of the SARS-CoV-2 incubation period. Further epidemiological investigations and clinical observations are urgently needed to identify the optimal incubation period of SARS-CoV-2 and formulate rational and evidence-based quarantine policies for COVID-19 accordingly.
Keywords: COVID-19; Case report; Incubation period; Quarantine duration; SARS-CoV-2.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Household secondary attack rate of COVID-19 and associated determinants in Guangzhou, China: a retrospective cohort study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;20(10):1141-1150. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30471-0. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32562601 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of hydroxychloroquine for post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection among adults exposed to coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 3;21(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04446-4. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32493478 Free PMC article.
-
A familial cluster of COVID-19 infection in a northern Chinese region.J Infect Public Health. 2021 Sep;14(9):1127-1132. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2021.07.011. Epub 2021 Jul 18. J Infect Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34343962 Free PMC article.
-
[Detection and evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid contamination in corona virus disease 19 ward surroundings and the surface of medical staff's protective equipment].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Oct 18;52(5):803-808. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.002. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 33047711 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review.JAMA. 2020 Aug 25;324(8):782-793. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12839. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 32648899 Review.
Cited by
-
Entity and relation extraction from clinical case reports of COVID-19: a natural language processing approach.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Jan 26;23(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02117-3. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 36703154 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing changes in incubation period, serial interval, and generation time of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med. 2023 Sep 29;21(1):374. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03070-8. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37775772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Novel coronavirus infection pneumonia is included in the management of notifiable infectious diseases. Available from: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/jkj/s7916/202001/44a3b8245e8049d2837a4f27529cd386.... .
-
- Adhikari SP, Meng S, Wu YJ, Mao YP, Ye RX, Wang QZ, Sun C, Sylvia S, Rozelle S, Raat H, Zhou H. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9:29. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous