Targeting ITK signaling for T cell-mediated diseases
- PMID: 34368657
- PMCID: PMC8326193
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102842
Targeting ITK signaling for T cell-mediated diseases
Abstract
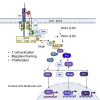
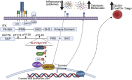
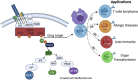
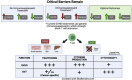
The focus of this review is to examine the role of ITK signaling in multiple diseases and investigate the clinical potential of ITK inhibition. The diseases and potential interventions reviewed include T cell-derived malignancies as well as other neoplastic diseases, allergic diseases such as asthma and atopic dermatitis, certain infectious diseases, several autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis, and finally the use of ITK inhibition in both solid organ and bone marrow transplantation recipients.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Biological sciences; Cell biology; Immunology; Molecular biology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Agostinelli C., Rizvi H., Paterson J., Shende V., Akarca A.U., Agostini E., Fuligni F., Righi S., Spagnolo S., Piccaluga P.P. Intracellular TCR-signaling pathway: novel markers for lymphoma diagnosis and potential therapeutic targets. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014;38:1349–1359. - PubMed
-
- Benson M., Mobini R., Barrenäs F., Halldén C., Naluai A.T., Säll T., Cardell L.O. A haplotype in the inducible T-cell tyrosine kinase is a risk factor for seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 2009;64:1286–1291. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

