JWES: a new pipeline for whole genome/exome sequence data processing, management, and gene-variant discovery, annotation, prediction, and genotyping
- PMID: 34370400
- PMCID: PMC8409305
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13261
JWES: a new pipeline for whole genome/exome sequence data processing, management, and gene-variant discovery, annotation, prediction, and genotyping
Abstract
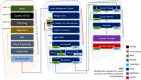
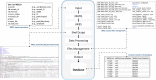
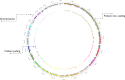
Whole genome and exome sequencing (WGS/WES) are the most popular next-generation sequencing (NGS) methodologies and are at present often used to detect rare and common genetic variants of clinical significance. We emphasize that automated sequence data processing, management, and visualization should be an indispensable component of modern WGS and WES data analysis for sequence assembly, variant detection (SNPs, SVs), imputation, and resolution of haplotypes. In this manuscript, we present a newly developed findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR) bioinformatics-genomics pipeline Java based Whole Genome/Exome Sequence Data Processing Pipeline (JWES) for efficient variant discovery and interpretation, and big data modeling and visualization. JWES is a cross-platform, user-friendly, product line application, that entails three modules: (a) data processing, (b) storage, and (c) visualization. The data processing module performs a series of different tasks for variant calling, the data storage module efficiently manages high-volume gene-variant data, and the data visualization module supports variant data interpretation with Circos graphs. The performance of JWES was tested and validated in-house with different experiments, using Microsoft Windows, macOS Big Sur, and UNIX operating systems. JWES is an open-source and freely available pipeline, allowing scientists to take full advantage of all the computing resources available, without requiring much computer science knowledge. We have successfully applied JWES for processing, management, and gene-variant discovery, annotation, prediction, and genotyping of WGS and WES data to analyze variable complex disorders. In summary, we report the performance of JWES with some reproducible case studies, using open access and in-house generated, high-quality datasets.
Keywords: bioinformatics application; database; gene; variants; whole exome; whole genome.
© 2021 The Authors. FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CoVaCS: a consensus variant calling system.BMC Genomics. 2018 Feb 5;19(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4508-1. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29402227 Free PMC article.
-
A community-based resource for automatic exome variant-calling and annotation in Mendelian disorders.BMC Genomics. 2014;15 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-S3-S5. Epub 2014 May 6. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25078076 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics pipelines to investigate susceptibility in whole genome and exome sequenced data for variant discovery, annotation, prediction and genotyping.PeerJ. 2021 Jul 26;9:e11724. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11724. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34395068 Free PMC article.
-
Added Value of Reanalysis of Whole Exome- and Whole Genome Sequencing Data From Patients Suspected of Primary Immune Deficiency Using an Extended Gene Panel and Structural Variation Calling.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 30;13:906328. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.906328. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35874679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Disease Sequence Data Resource (MSeqDR): a global grass-roots consortium to facilitate deposition, curation, annotation, and integrated analysis of genomic data for the mitochondrial disease clinical and research communities.Mol Genet Metab. 2015 Mar;114(3):388-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.11.016. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Mol Genet Metab. 2015. PMID: 25542617 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches using gene expression and variant data for personalized medicine.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Sep 20;23(5):bbac191. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac191. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 35595537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resources and tools for rare disease variant interpretation.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 10;10:1169109. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1169109. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37234922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional mutation, splice, distribution, and divergence analysis of impactful genes associated with heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 5;13(1):16769. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44127-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37798313 Free PMC article.
-
VAREANT: a bioinformatics application for gene variant reduction and annotation.Bioinform Adv. 2024 Dec 31;5(1):vbae210. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbae210. eCollection 2025. Bioinform Adv. 2024. PMID: 39927292 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated ACMG-approved genes and ICD codes for the translational research and precision medicine.Database (Oxford). 2023 May 17;2023:baad033. doi: 10.1093/database/baad033. Database (Oxford). 2023. PMID: 37195695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meyers BC, Scalabrin S and Morgante M (2004) Mapping and sequencing complex genomes: let's get physical! Nat Rev Genet 5, 578–588. - PubMed
-
- Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EWet al. (2001) The sequence of the human genome. Science 291, 1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, 860–921. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

