Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Expression Profiling Revealed Its Role in Regulating Stress Responses in Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- PMID: 34371574
- PMCID: PMC8309457
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10071371
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Expression Profiling Revealed Its Role in Regulating Stress Responses in Potato (Solanum tuberosum)
Abstract
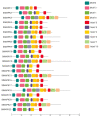
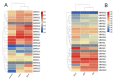
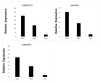
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades are the universal signal transduction networks that regulate cell growth and development, hormone signaling, and other environmental stresses. However, their essential contribution to plant tolerance is very little known in the potato (Solanum tuberosum) plant. The current study carried out a genome-wide study of StMAPK and provided a deep insight using bioinformatics tools. In addition, the relative expression of StMAPKs was also assessed in different plant tissues. The similarity search results identified a total of 22 StMAPK genes in the potato genome. The sequence alignment also showed conserved motif TEY/TDY in most StMAPKs with conserved docking LHDXXEP sites. The phylogenetic analysis divided all 22 StMAPK genes into five groups, i.e., A, B, C, D, and E, showing some common structural motifs. In addition, most of the StMAPKs were found in a cluster form at the terminal of chromosomes. The promoter analysis predicted several stress-responsive Cis-acting regulatory elements in StMAPK genes. Gene duplication under selection pressure also indicated several purifying and positive selections in StMAPK genes. In potato, StMAPK2, StMAPK6, and StMAPK19 showed a high expression in response to heat stress. Under ABA and IAA treatment, the expression of the total 20 StMAPK genes revealed that ABA and IAA played an essential role in this defense process. The expression profiling and real-time qPCR (RT-qPCR) exhibited their high expression in roots and stems compared to leaves. These results deliver primary data for functional analysis and provide reference data for other important crops.
Keywords: RT-qPCR; StMAPKs; TXY motifs; expression; genome-wide; phylogeny.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Expression profiling of pathogenesis-related Protein-1 (PR-1) genes from Solanum tuberosum reveals its critical role in phytophthora infestans infection.Microb Pathog. 2021 Dec;161(Pt B):105290. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105290. Epub 2021 Nov 20. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34808276
-
A comprehensive expression analysis of the expansin gene family in potato (Solanum tuberosum) discloses stress-responsive expansin-like B genes for drought and heat tolerances.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 18;14(7):e0219837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219837. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31318935 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of DUF221 Gene Family Provides New Insights Into Abiotic Stress Responses in Potato.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 20;12:804600. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.804600. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35126430 Free PMC article.
-
Sucrose non-ferment 1 related protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) genes could mediate the stress responses in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.).BMC Genet. 2017 May 15;18(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12863-017-0506-6. BMC Genet. 2017. PMID: 28506210 Free PMC article.
-
MYB Gene Family in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.): Genome-Wide Identification of Hormone-Responsive Reveals Their Potential Functions in Growth and Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 29;20(19):4847. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194847. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31569557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters expression profiling revealed its role in the development and regulating stress response in Solanum tuberosum.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):5251-5264. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06697-z. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34480688
-
Mechanisms of salinity tolerance and their possible application in the breeding of vegetables.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Mar 14;23(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04152-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36915096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Characterization of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Gene Family and Their Expression Patterns in Response to Drought and Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides in Walnut (Juglans regia).Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 29;12(3):586. doi: 10.3390/plants12030586. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771674 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiling of DUF668 Genes in Glycine max under Salt Stress.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;12(16):2923. doi: 10.3390/plants12162923. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631135 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in potato under biotic and abiotic stress.Mol Breed. 2022 Jun 11;42(6):31. doi: 10.1007/s11032-022-01302-y. eCollection 2022 Jun. Mol Breed. 2022. PMID: 37312964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

