Maternal Nutrition Status Associated with Pregnancy-Related Adverse Outcomes
- PMID: 34371906
- PMCID: PMC8308922
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13072398
Maternal Nutrition Status Associated with Pregnancy-Related Adverse Outcomes
Abstract
Although maternal nutrition has an impact on fetal development and gestational outcome, tracking maternal nutrition in outpatient practice is still complex and involves proper technical capacitation in this area. Nevertheless, the association between nutritional variables may broaden the ability to predict the occurrence of gestational disorders and prevention management. We aimed to identify factors that could indicate the probability of adverse outcomes in mid-pregnancy. From a cohort of 1165 nulliparous pregnant women without any previous disease, the nutritional status was assessed by body mass index (BMI) and mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC), associated with dietary patterns and sociodemographic characteristics. Two predictive models with nutritional status for screening the occurrence of adverse outcomes of preterm birth, gestational diabetes mellitus, small-for-gestational-age newborns and preeclampsia were developed. The odds of adverse outcomes were higher in non-white (p < 0.05) obese women and with high protein consumption. There was no significant difference between the models, with an overall accuracy of 63% for both models and a probability of success in predicting adverse outcomes (BMI = 61%, MUAC = 52%). This study of Brazilian pregnant nulliparous women offers two possible options for early tracking of adverse gestational outcomes that should be further externally validated.
Keywords: gestational diabetes mellitus; maternal nutrition; preeclampsia; preterm birth; small-for-gestational-age.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
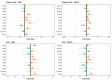
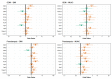
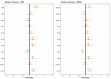
References
-
- Hashmi A.H., Solomon N., Lee S.J., Min A.M., Gilder M.E., Wiladphaingern J., Tun N.W., Plugge E., Wickramasinghe K., Angkurawaranon C., et al. Nutrition in transition: Historical cohort analysis summarising trends in under- and over-nutrition among pregnant women in a marginalised population along the Thailand-Myanmar border from 1986 to 2016. Br. J. Nutr. 2019;121:1413–1423. doi: 10.1017/S0007114519000758. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miele M.J.O., Souza R.T., Calderon I.M., Feitosa F.E., Leite D.F., Filho E.A.R., Vettorazzi J., Mayrink J., Vieira M.C., Pacagnella R.C., et al. Profile of calories and nutrients intake in a Brazilian multicenter study of nulliparous women. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021 doi: 10.1002/ijgo.13655. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

