Use of Different Food Classification Systems to Assess the Association between Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Cardiometabolic Health in an Elderly Population with Metabolic Syndrome (PREDIMED-Plus Cohort)
- PMID: 34371982
- PMCID: PMC8308804
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13072471
Use of Different Food Classification Systems to Assess the Association between Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Cardiometabolic Health in an Elderly Population with Metabolic Syndrome (PREDIMED-Plus Cohort)
Abstract
The association between ultra-processed food (UPF) and risk of cardiometabolic disorders is an ongoing concern. Different food processing-based classification systems have originated discrepancies in the conclusions among studies. To test whether the association between UPF consumption and cardiometabolic markers changes with the classification system, we used baseline data from 5636 participants (48.5% female and 51.5% male, mean age 65.1 ± 4.9) of the PREDIMED-Plus ("PREvention with MEDiterranean DIet") trial. Subjects presented with overweight or obesity and met at least three metabolic syndrome (MetS) criteria. Food consumption was classified using a 143-item food frequency questionnaire according to four food processing-based classifications: NOVA, International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), International Food Information Council (IFIC) and University of North Carolina (UNC). Mean changes in nutritional and cardiometabolic markers were assessed according to quintiles of UPF consumption for each system. The association between UPF consumption and cardiometabolic markers was assessed using linear regression analysis. The concordance of the different classifications was assessed with intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC3, overall = 0.51). The highest UPF consumption was obtained with the IARC classification (45.9%) and the lowest with NOVA (7.9%). Subjects with high UPF consumption showed a poor dietary profile. We detected a direct association between UPF consumption and BMI (p = 0.001) when using the NOVA system, and with systolic (p = 0.018) and diastolic (p = 0.042) blood pressure when using the UNC system. Food classification methodologies markedly influenced the association between UPF consumption and cardiometabolic risk markers.
Keywords: IARC; IFIC; NOVA; PREDIMED-Plus; UNC; cardiometabolic risk; classification systems; diet; food processing; ultra-processed food.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S.-S. reports serves on the board of, and receives grant support through, his institution from the International Nut and Dried Fruit Council and Eroski Foundation; serves on the Executive Committee of the Instituto Danone Spain and on the Scientific Committee of the Danone International Institute; receives research support from Patrimonio Comunal Olivarero (Spain) and Borges S.A. (Spain); and receives consulting fees or travel expenses from Danone, Font Vella, Lanjarón, Nuts For Life, Eroski Foundation, Instituto Danone (Spain) and Abbot Laboratories. E.R. reports grants, non-financial support and other fees from California Walnut Commission and Alexion; personal fees and non-financial support from Merck, Sharp and Dohme; personal fees, non-financial support and other fees from Aegerion, and Ferrer International; grants and personal fees from Sanofi Aventis; grants from Amgen and Pfizer; and personal fees from Akcea, outside of the submitted work. X.P. serves on the board of, and receives consulting personal fees from, Sanofi Aventis, Amgen and Abbott Laboratories; and receives personal lecture fees from Esteve, Lacer and Rubio laboratories.
Figures
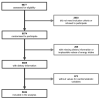
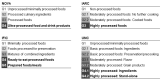
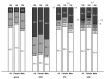
References
-
- Fardet A. Food health potential is primarily due to its matrix structure, then nutrient composition: A new paradigm for food classification according to technological processes applied. J. Nutr. Health Food Eng. 2014;1:208–209. doi: 10.15406/jnhfe.2014.01.00031. - DOI
-
- Fardet A. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. Volume 85. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. Characterization of the Degree of Food Processing in Relation with Its Health Potential and Effects; pp. 79–129. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- #340918/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- PI13/00673, PI13/00492, PI13/00272, PI13/01123, PI13/00462, PI13/00233, PI13/02184, PI13/00728, PI13/01090, PI13/01056, PI14/01722, PI14/00636, PI14/00618, PI14/00696, PI14/01206, PI14/01919, PI14/00853, PI14/01374, PI14/00972, PI14/00728, PI14/01471/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red-Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición
- PI16/00473, PI16/00662, PI16/01873, PI16/01094, PI16/00501, PI16/00533, PI16/00381, PI16/00366, PI16/01522, PI16/01120, PI17/00764, PI17/01183, PI17/00855, PI17/01347, PI17/00525, PI17/01827, PI17/00532, PI17/00215, PI17/01441/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red-Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición
- PI17/00508, PI17/01732, PI17/00926, PI19/00957, PI19/00386, PI19/00309, PI19/01032, PI19/00576, PI19/00017, PI19/01226, PI19/00781, PI19/01560, PI19/01332/Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red-Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición

