Conception of a Phantom in Agar-Agar Gel with the Same Bio-Impedance Properties as Human Quadriceps
- PMID: 34372435
- PMCID: PMC8347085
- DOI: 10.3390/s21155195
Conception of a Phantom in Agar-Agar Gel with the Same Bio-Impedance Properties as Human Quadriceps
Abstract
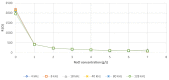
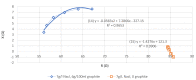
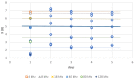
The physiology of the patient can be reflected by various data. Serious games, using an intelligent combination, could be based on this data to adjust to the specificities of the patient. Rehabilitation would therefore be personalized to the patient. This smart suit would use dry electrodes in order to be easily usable. Before performing dry electrode validation tests on a population, it is necessary to perform preliminary tests on a phantom. Agar-Agar (AA) gel, combined with NaCl and graphite which directly impact the resistivity and reactance values of the phantom, are generally used. Depending on the part of the body simulated by the phantom, it is necessary to adapt the concentrations of NaCl and graphite in order to obtain values of physiological reactance and resistance. The anisotropy of a muscle must also be considered. Different concentrations of NaCl and graphite have been tested in order to present charts linking the concentrations to the resistance and reactance values of the AA phantom. Electrical properties similar to those of human quadriceps are achieved at a concentration of 7 g/L of NaCl and 60 g/L of graphite. These values can be used as a conversion table to develop an AA phantom with electrical properties similar to different muscles. Furthermore, an AA phantom has an anisotropy of 0° and 90°. This anisotropy corresponds to a human quadriceps, where 0° is the direction of the muscle fiber. This will allow us to study and characterize the behavior of the electrodes on an anisotropic model. Thus it can be used as a first test phase for dry electrodes in order to propose the most suitable conditions for a connected garment application.
Keywords: NaCl; agar-agar; bioimpedance; graphite; muscle; phantom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Eco-Friendly Bioimpedance Muscle Phantom: PVA-Agar Hydrogel Mimicking Living Tissue at Low Frequencies.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2024 Jul;2024:1-4. doi: 10.1109/EMBC53108.2024.10782661. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2024. PMID: 40039341
-
A versatile high-permittivity phantom for EIT.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008 Nov;55(11):2601-7. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2008.2001287. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2008. PMID: 18990630 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a high-hydrous gel phantom for human body communication based on electrical anisotropy.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2019 Jul;2019:4028-4031. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2019.8857862. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2019. PMID: 31946755
-
Detection of emboli in vessels using electrical impedance measurements--phantom and electrodes.Physiol Meas. 2005 Apr;26(2):S111-8. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/26/2/011. Epub 2005 Mar 29. Physiol Meas. 2005. PMID: 15798224
-
A controllably anisotropic conductivity or diffusion phantom constructed from isotropic layers.Ann Biomed Eng. 2009 Dec;37(12):2522-31. doi: 10.1007/s10439-009-9799-6. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009. PMID: 19760146 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multifrequency electrical impedance tomography (Mf-EIT) for the detection of breast cancer phantom anomalies.MethodsX. 2024 Dec 6;14:103087. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2024.103087. eCollection 2025 Jun. MethodsX. 2024. PMID: 39758433 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abt C. Serious Games. The Viking Press; New York, USA: 1970.
-
- Alvarez J., Djaouti D. Introduction au Serious Game. Questions théoriques; Paris, France: 2010.
-
- Lavergne Boudier V., Dambach Y. Serious Game: Révolution Pédagogique. Hermes-Lavoisier; Cachan, France: 2010.
-
- Michael D., Chen S. Serious Games. Games that Educate, Train and Inform. Course Technology PTR; Boston, MA, USA: 2005.
-
- Schmoll P. Jeux sérieux: Exploration d’un oxymore. Rev. Des. Sci. Soc. 2011;45:158–167.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

