Psoriasis epidemiology screening tool (PEST) is useful for the detection of psoriatic arthritis in the Japanese population
- PMID: 34373544
- PMCID: PMC8352892
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-95620-4
Psoriasis epidemiology screening tool (PEST) is useful for the detection of psoriatic arthritis in the Japanese population
Abstract
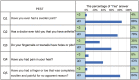
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that involves various systemic organs and tissues and is characterized by scaly erythematous skin. Among the different types of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is frequently reported, and occasionally develops into severe arthritis leading to joint dysfunction. There are various tools, especially questionnaires, to identify the presence of PsA in European and American populations; however, little is known about the utility of these tools in the Asian population. In this study, we investigated the utility of a representative tool, the psoriasis epidemiology screening tool (PEST) questionnaire, to identify PsA among Japanese patients with psoriasis. A total of 143 patients with psoriasis were enrolled in this study. Among them, 29 patients were diagnosed with PsA. The frequency of PsA was significantly increased in patients with PEST scores > 3, with a sensitivity of 93.1% and a specificity of 78.9%. Among the questions in the PEST questionnaire, "Have you ever had a swollen joint?" showed the highest frequency to answer "Yes" among patients with PsA. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that high PEST scores (> 3) was an independent variable in PsA patients. Taken together, our study suggests that the PEST questionnaire is a useful tool to identify PsA among Japanese patients with psoriasis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High prevalence of psoriatic arthritis in patients with severe psoriasis with suboptimal performance of screening questionnaires.Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 May;72(5):736-40. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201706. Epub 2012 Jun 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013. PMID: 22730367
-
Prevalence of Psoriatic Arthritis in Nagano Prefecture, Japan, and Efficacy of the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool: A Real-World Survey.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2022 Jun 25;257(3):205-210. doi: 10.1620/tjem.2022.J035. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35491123
-
Evaluating the Persian versions of two psoriatic arthritis screening questionnaires early arthritis for psoriatic patients questionnaire (EARP) and psoriasis epidemiology screening tool (PEST) in Iranian psoriatic patients.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 26;51(1):159-166. doi: 10.3906/sag-2006-372. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 32927935 Free PMC article.
-
Development of screening tools to identify psoriatic arthritis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2010 Aug;12(4):295-9. doi: 10.1007/s11926-010-0113-2. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20617467 Review.
-
Psoriatic arthritis screening: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Apr 1;58(4):692-707. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key314. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30380111 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Analysis of PEST Questionnaire Responses in Patients with Psoriasis in Daily Practice: Results from a Single-Center of Psoriasis in the Czech Republic.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025 Apr;15(4):819-829. doi: 10.1007/s13555-025-01374-6. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40032792 Free PMC article.
-
Patient perceptions of psoriatic disease in Japan: Results from the Japanese subgroup of the Understanding Psoriatic Disease Leveraging Insights for Treatment (UPLIFT) survey.J Dermatol. 2022 Sep;49(9):818-828. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16423. Epub 2022 May 27. J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35624553 Free PMC article.
-
Screening Tools for Spondyloarthritis in Patients With Psoriasis, Uveitis, and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Scoping Review.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024 Jun;76(6):860-870. doi: 10.1002/acr.25308. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38303576 Free PMC article.
-
Advantages of ultrasound imaging for the early diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 4;10(13):e34136. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34136. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39055795 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis and Systemic Inflammatory Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 18;23(8):4457. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084457. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous